Figure 2.
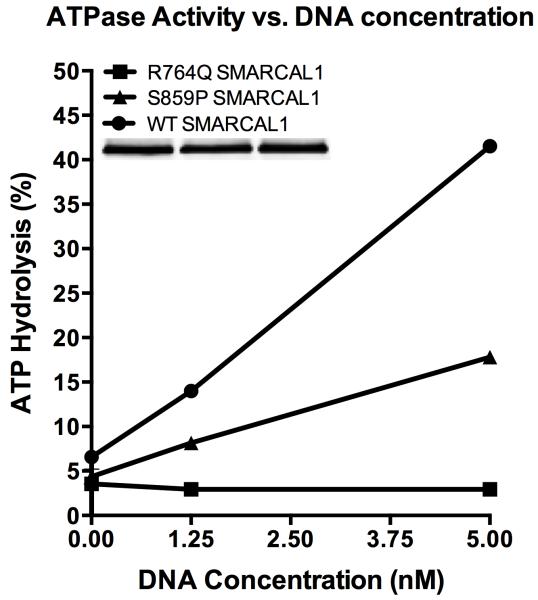
To purify SMARCAL1 from human cells, HEK-293T cells were transfected with pLPCX-Flag-SMARCAL1, pLPCX-Flag-S859P SMARCAL1, or pLPCX-Flag-R764Q SMARCAL1 plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). The latter two destination vectors were made by site directed mutagenesis of pENTR-SMARCAL1 with an 11x wobble mutation and then cloned into the pLPCX vector using the Clonase system (Invitrogen). Seventy-two hours after transfection, the cells were lysed in NETN buffer (150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris pH 8, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5% IGEPAL CA-630) for 30 min on ice. After high-speed centrifugation, the cleared lysates were incubated with Flag-M2 beads (Sigma) for 3 h at 4°C. The beads were washed three times in NETN lysis buffer and twice in SMARCAL1 buffer (20 mM HEPES at pH 7.6, 20% glycerol, 0.1 M KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 0.2 mM PMSF, 0.01% IGEPAL CA-630). The bound proteins were eluted in SMARCAL1 buffer containing 0.3 mg/mL Flag peptide on ice, flash-frozen, and stored at −80°C. For the ATPase assay increasing concentrations of oligonucleotides (0, 1.25, or 5 nM final concentration) were incubated with purified SMARCAL1 (5 nM final concentration) in a final volume of 10 μL, and the reactions were incubated for 30 minutes at 30°C. The results are presented as the percent ATP hydrolyzed during the reaction. The assay was performed at least three times with the graph depicting means and standard deviation error bars. The splayed arm DNA substrate used in this assay was prepared by annealing the following two oligonucleotides: CCAGTGAATTGTTGCTCGGTACCTGCTAAC and GACATTTGATACCGAGCAACAATTCACTGG. The differences between the S859P SMARCAL1 and WT SMARCAL1 curves were significant at all oligonucleotide concentrations by two-way ANOVA. The differences between the R764Q SMARCAL1 and S859P SMARCAL1 curves were significant at 1.25 nM and 5 nM oligonucleotide concentrations by two-way ANOVA.