Abstract
Increased calcium (Ca) excretion is characteristic of chronic phosphate (PO4) depletion (PD). To study the changes in tubular transport and the site of the hypocalciuric effect of PO4 administration, clearance and micropuncture experiments were performed in intact rats pair fed either a control diet (0.5% PO4) or a PO4-depleted (PD) diet (0.01% PO4) plus Al(OH3) and in parathyroidectomized (PTX) PD rats, infused either with saline or with neutral sodium PO4.
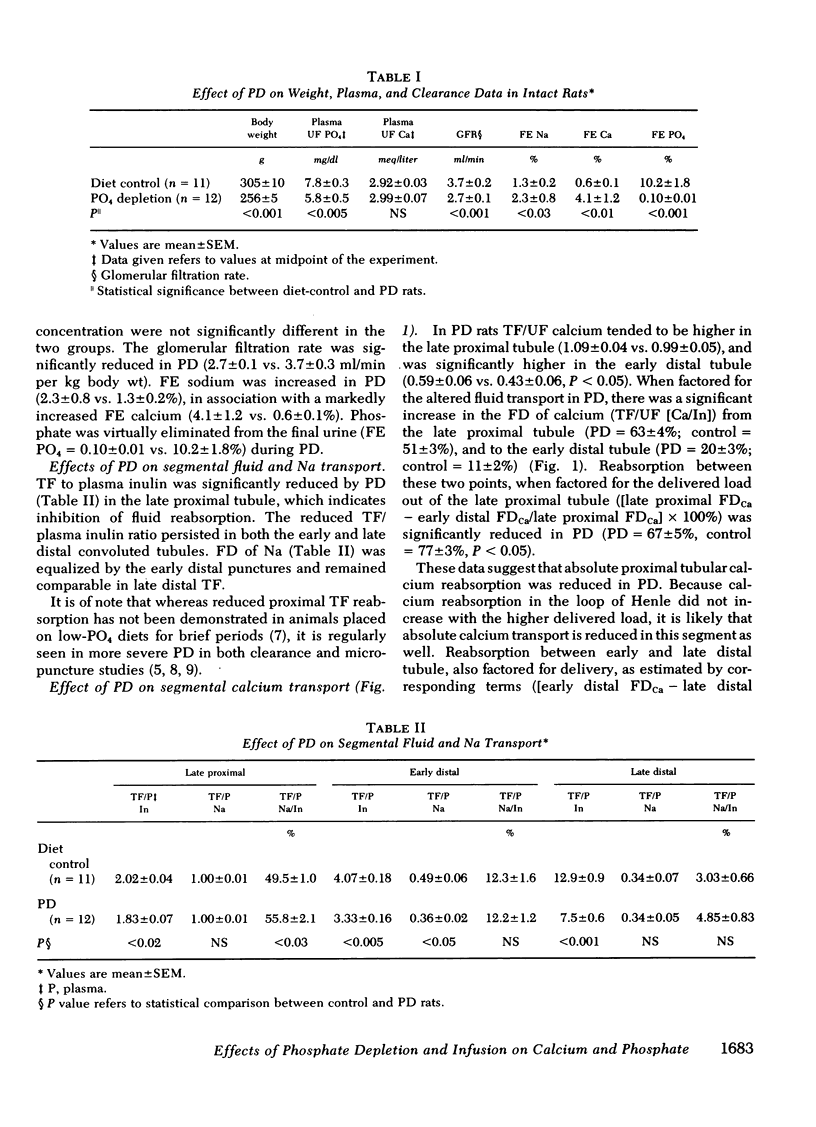
Intact PD rats, compared with intact rats on a control diet, exhibited a lower plasma ultrafiltrable (UF) PO4 (5.8±0.5 vs. 7.8±0.3 mg/dl), higher fractional excretion (FE) of Ca (4.1±1.2 vs. 0.6±0.1%), and reduced FE PO4 (0.1±0.01 vs. 10.2±1.8%). Tubular fluid/plasma inulin was lower in the late proximal tubule of PD rats, associated with increases in fractional delivery (FD) from the proximal tubule of Na and Ca.
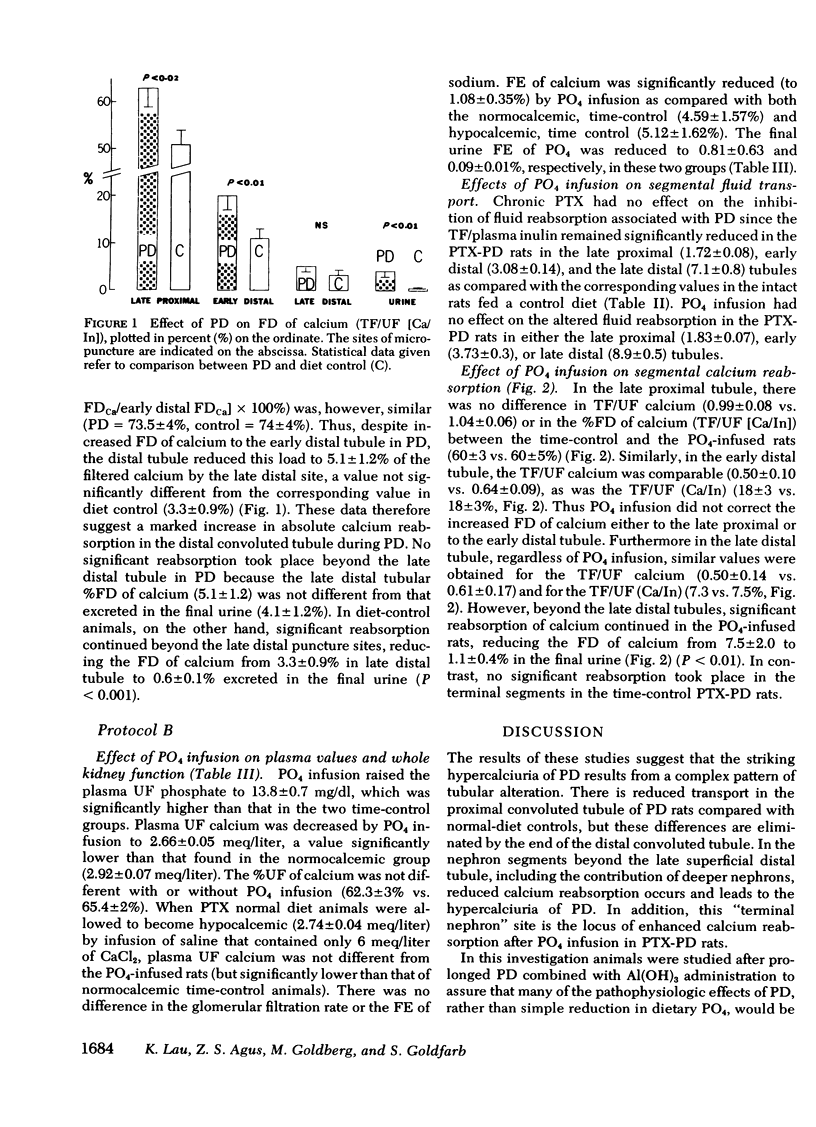
The%FD of Ca to the early distal tubule of PD rats was increased (20±3 vs. 11±2%), but this difference was abolished by the late distal tubule (5.1±1.2 vs. 3.3±0.9%). In PTX-PD rats, PO4 infusion increased plasma UF PO4 (13.8±0.7 vs. 7.8±0.7 mg/dl). FE of Ca was reduced (1.08±0.35 vs. 4.59±1.57%) without correcting the increased Ca delivery to the late distal tubule.
These data indicate that PD impairs Ca reabsorption in tubular segments before but not within the distal convoluted tubule, so that hypercalciuria is ultimately a result of decreased Ca transport either in the terminal nephron or in deeper nephrons where PO4 infusion stimulates Ca transport independent of parathyroid hormone or changes in the filtered load of Ca.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agus Z. S., Chiu P. J., Goldberg M. Regulation of urinary calcium excretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jun;232(6):F545–F549. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.6.F545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabardès D., Imbert M., Clique A., Montégut M., Morel F. PTH sensitive adenyl cyclase activity in different segments of the rabbit nephron. Pflugers Arch. 1975;354(3):229–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00584646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn J. W., Massry S. G. Changes in serum and urinary calcium during phosphate depletion: studies on mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1073–1087. doi: 10.1172/JCI106323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo L. S., Windhager E. E. Calcium and sodium transport by the distal convoluted tubule of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):F492–F506. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.5.F492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez J. H., Gray R. W., Lemann J., Jr Dietary phosphate deprivation in women and men: effects on mineral and acid balances, parathyroid hormone and the metabolism of 25-OH-vitamin D. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;43(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-5-1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmett M., Goldfarb S., Agus Z. S., Narins R. G. The pathophysiology of acid-base changes in chronically phosphate-depleted rats: bone-kidney interactions. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):291–298. doi: 10.1172/JCI108640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein F. O., Kliger A. S. Medullary structures in calcium reabsorption in rats with renal insufficiency. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):F197–F200. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.3.F197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. W., Massry S. G., Arieff A. I., Coburn J. W. Renal bicarbonate wasting during phosphate depletion. A possible cause of altered acid-base homeostasis in hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2556–2561. doi: 10.1172/JCI107447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. W., Massry S. G., Friedler R. M. Effect of phosphate depletion on renal tubular reabsorption of glucose. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Mar;89(3):554–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb S., Westby G. R., Goldberg M., Agus Z. S. Renal tubular effects of chronic phosphate depletion. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):770–779. doi: 10.1172/JCI108698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K., Goldfarb S., Grabie M., Agus Z. S., Goldberg M. Mechanism of lithium-induced hypercalciuria in rats. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):E294–E300. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.3.E294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grimellec C., Roinel N., Morel F. Simultaneous Mg, Ca, P, K and Cl analysis in rat tubular fluid. IV. During acute phosphate plasma loading. Pflugers Arch. 1974;346(3):189–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00595706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grimellec C., Roinel N., Morel F. Simultaneous Mg, Ca, P, K, Na and Cl analysis in rat tubular fluid. 3. During acute Ca plasma loading. Pflugers Arch. 1974;346(3):171–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00595705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlbauer R. C., Bonjour J. P., Fleisch H. Tubular localization of adaptation to dietary phosphate in rats. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):F342–F348. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.4.F342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poujeol P., Chabardes D., Roinel N., De Rouffignac C. Influence of extracellular fluid volume expansion on magnesium, calcium and phosphate handling along the rat nephron. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Sep 30;365(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1007/BF01067020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha A. S., Magaldi J. B., Kokko J. P. Calcium and phosphate transport in isolated segments of rabbit Henle's loop. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):975–983. doi: 10.1172/JCI108720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shareghi G. R., Stoner L. C. Calcium transport across segments of the rabbit distal nephron in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Oct;235(4):F367–F375. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.4.F367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen S. F., Boynar J. W., Jr, Stoll R. W. Effect of phosphate deprivation on renal phosphate transport in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):F199–F206. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.3.F199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


