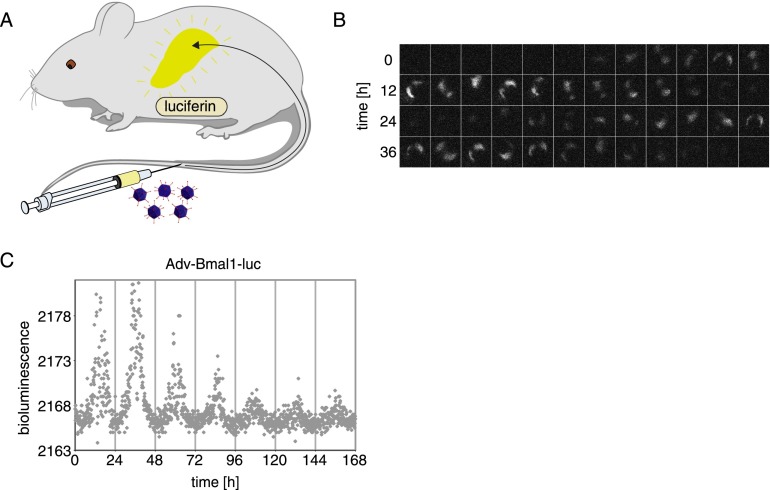
Figure 2.
Real-time recording of hepatic Adv-Bmal1-luc expression with a CCD camera. (A) Cartoon showing the preparation of a mouse for real-time bioluminescence imaging. The mouse was injected with 1 × 1011 infectious Adv-Bmal1-luc particles into the tail vein, and a osmotic minipump (model 2001, Alzet) containing a concentrated luciferin solution (90 mg/mL) was implanted into the intraperitoneal cavity (see the Materials and Methods). (B) Real-time imaging of bioluminescence emitted from the liver. A movie (exposure time, 30 sec) was taken during 48 h. The frames were inspected manually, and a picture was selected for each hour in which the mouse was immobile during the exposure time. The intervals between the selected frames were between 20 and 100 min. (C) Gray dots indicate time-integrated bioluminescence photon counts (30-sec EM-CCD exposure time) averaged over 7.5-min intervals as a function of time. Data were corrected for isolated high-intensity signal outliers (i.e., cosmic rays) (see the Materials and Methods).