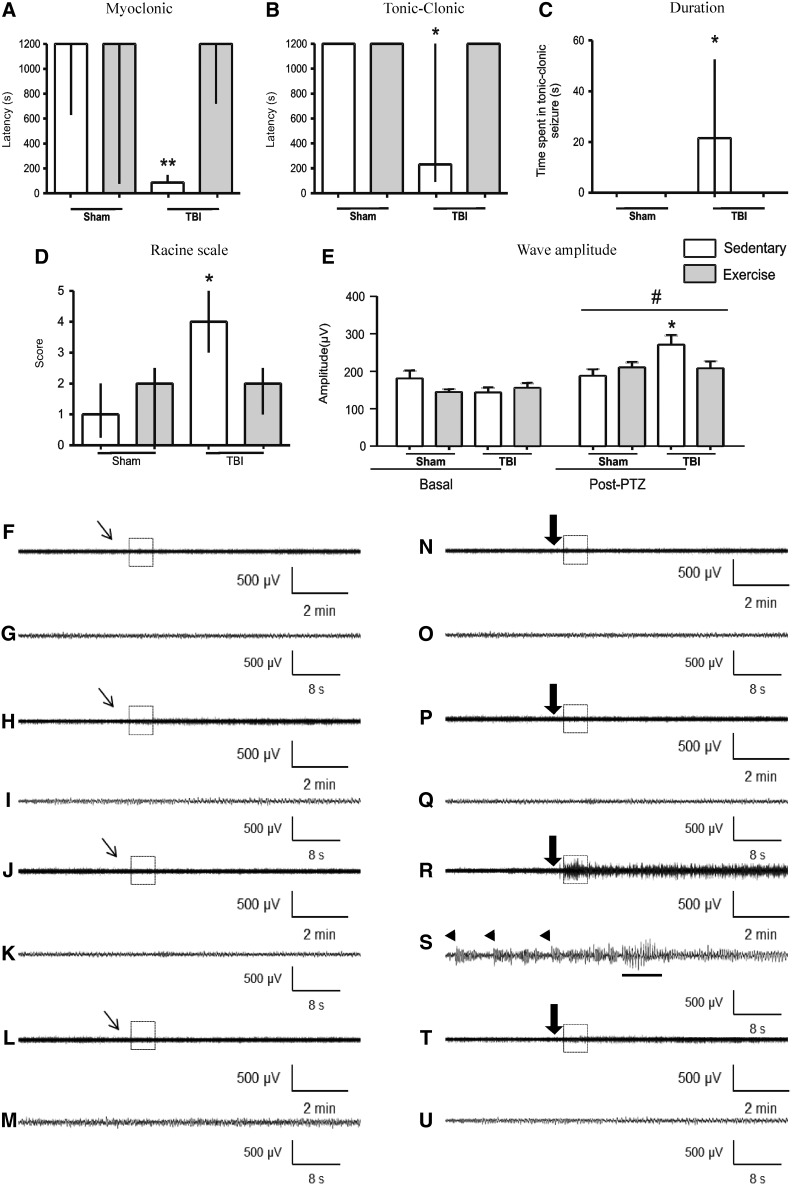
FIG. 2.
Effect of 4-week physical exercise started 1 week after TBI in seizure susceptibility with PTZ (35 mg/kg, intraperitoneally). Data from latency to the first myoclonic seizure (A), first tonic-clonic seizure (B), time spent in generalized tonic-clonic seizure (C), and Racine scale (D) are median±interquartile range. Data from wave amplitude analysis (E) are mean±standard error of the mean; all for n=8–11 per group. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01, compared with sham-sedentary, sham-exercise, and TBI-exercise (Scheirer-Ray-Hare and two-way ANOVA tests). #p<0.001, compared with basal period (two-way repeated measures ANOVA). Representative EEG recordings from ipsilateral parietal cortex after administration of saline (F-M) and PTZ (N-U), with their respective expanded waveforms outlined by boxes of sham-sedentary (F-G, N-O), sham-exercise (H-I, P-Q), TBI-sedentary (J-K, R-S), and TBI-exercise (L-M, T-U) groups. Inclined thin arrows indicate saline administration; large arrows indicate PTZ injection. Arrowheads indicate myoclonic seizure. Tonic-clonic seizure is indicated with an underlying trace. TBI, traumatic brain injury; ANOVA, analysis of variance; EEG, electroencephalogram; PTZ, pentylenetetrazol.