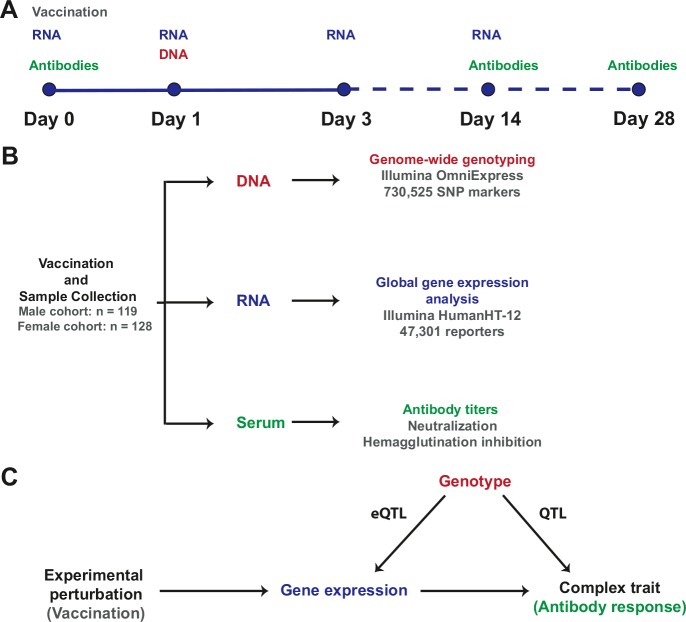
Figure 8. Study design and integrative analysis scheme.
(A) Individuals were immunized on day 0 and peripheral blood RNA samples were obtained on days 0, 1, 3, and 14. Antibody titers were measured on pre-immune sera and on days 14 and 28. Genotyping was carried out on a peripheral blood genomic DNA sample obtained on day 1. Identical sample collection schemes were used, 1 year apart, for the discovery (males) and validation (females) cohorts. (B) Sample sizes and data generation platforms. (C) Integrative analysis involved identification of loci that exhibit a transcriptional response to vaccination, evidence of genetic regulation of expression (constitutive eQTL), evidence of correlation between gene expression and the antibody response, and evidence of correlation between genotype and the antibody response (QTL). Because transcript abundance was measured serially, we were able to evaluate changes in the magnitude of the genetic effect on expression at different time points following vaccination. In addition, the study design permitted QTL analysis conditional on gene expression, which led to the identification of loci whose genetic effects on the antibody response are causally linked through the eQTL.