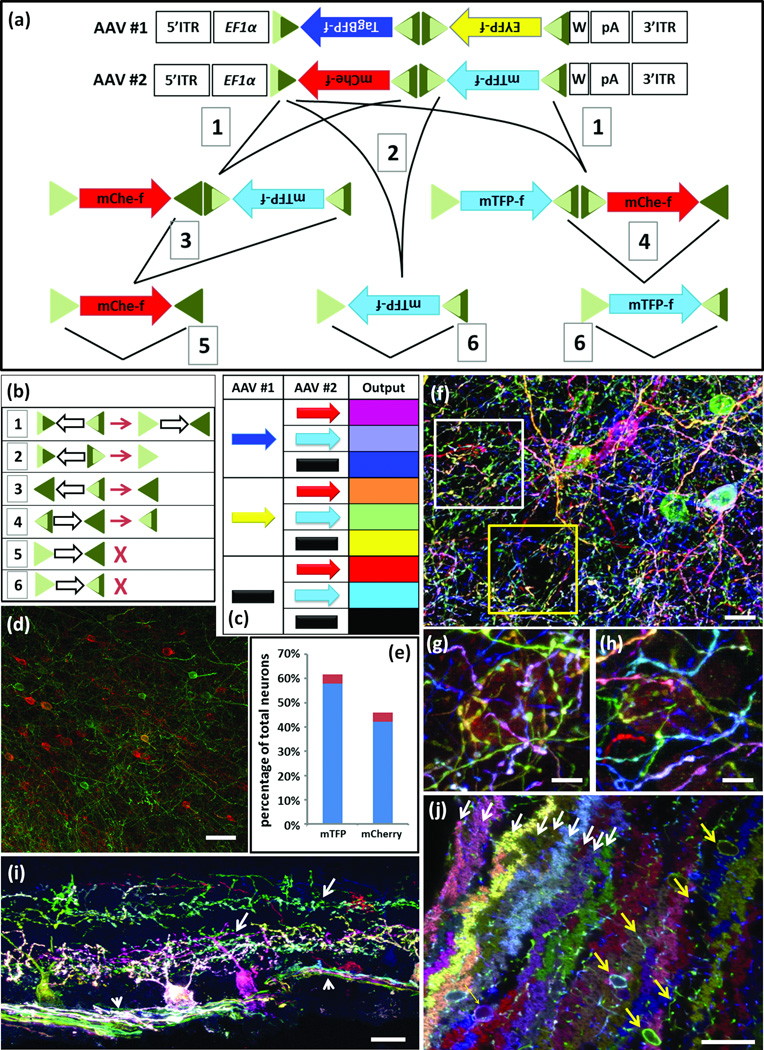
Figure 5. Brainbow AAV.
(a) AAV Brainbow constructs and recombination scheme. Farnesylated TagBFP and EYFP or mCherry and mTFP were placed in reverse orientation between mutant Lox sites. EF1α, regulatory elements from elongation factor 1α gene; W, WPRE; triangles, Lox mutants and their recombination products; dark and light sectors indicate wild-type and mutant portions of Lox sites, respectively; 1–6, recombination events.
(b) Outcomes of recombination events numbered in a. Open arrows, direction of intervening cDNA; X, fully mutant (light green) lox site cannot serve as substrate for Cre.
(c) Eight color outcomes resulting from pairs of Brainbow AAVs following recombination as shown in a. This is a minimum value, because it does not account for differences in relative intensity of the four XFPs
(d,e) Test of color balance. The mTFPf-mCherryf AAV vector was injected at low titer into the cortex of a Thy1-Cre mouse and neurons of each color were counted. Similar fractions of neurons expressed mTFPf (58%) and mCherryf (42%; n=1523 neurons in 4 sections of three mice; red shows standard deviation.)
(f–h) AAV injected into cortex of PV-cre mice predominantly labels interneurons. g and h, high magnification views of boxed regions in f.
(i) AAV injected into retina of mouse expressing Cre in retinal ganglion cell subset shows labeling of ganglion cell somata, dendrites (arrow) and axons (arrowhead).
(j) AAV injected into cerebellum of PV-Cre mouse labels Purkinje cells (fan shaped dendrites, white arrows) and interneurons (cell bodies and axons, yellow arrows).
In f–j antibody amplified mTFP and EYFP were in green; TagBFP was in blue and mCherry was in red.
Bars are 20µm in f, 10µm in g and h, 50µm in i and j