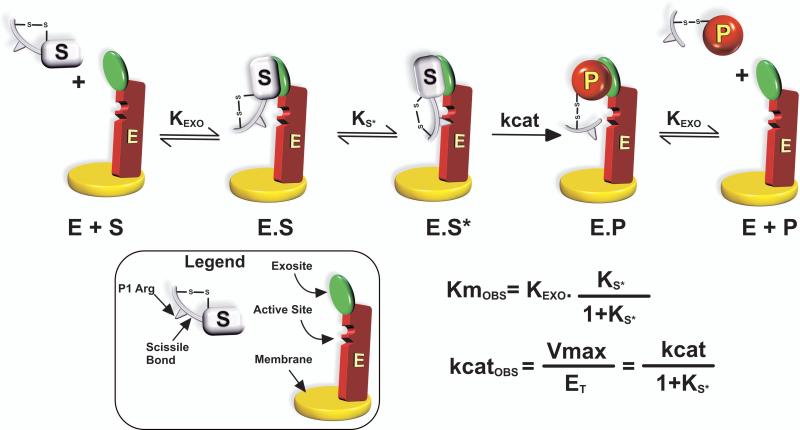
Figure 3. Multi-step Pathway for Protein Substrate Recognition by Prothrombinase.
Kinetic scheme resolved for the action of prothrombinase on P2. The initial binding interaction between substrate (S) and prothrombinase (E) to form ES results from exosite-dependent interactions between S and E. Exosite binding is followed by a unimolecular binding step in which structures flanking the cleavage site engage the active-site of the enzyme before catalysis can occur. The product (P) is also bound to E by exosite interactions before it is released. The graphical legend highlights the important features of S and E. The composite nature of the steady state kinetic constants is illustrated by derivation employing the rapid equilibrium assumption. Ks* is defined as [E.S]/[E.S*].