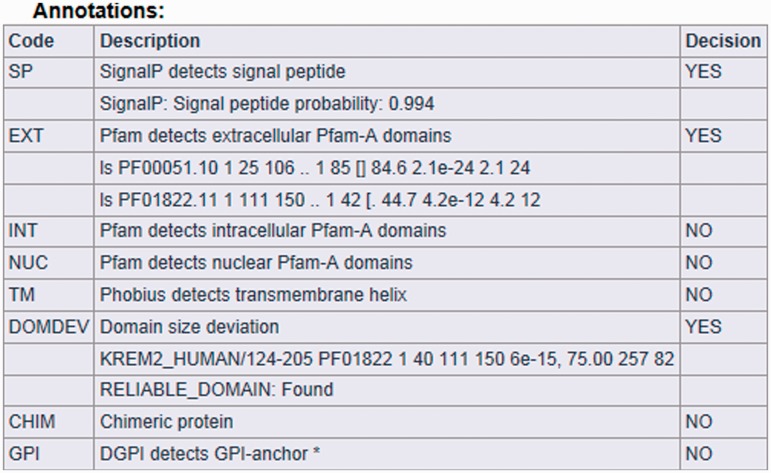
Figure 3.
MisPred analysis of a protein sequence for potential sequence errors. The sequence shown in Figure 1 was analysed with the various MisPred tools. The figure shows the primary conclusions based on the analyses for signal peptide, Pfam-A domains, transmembrane helix, GPI anchor, domain-size integrity and chromosomal localization of the exons encoding the protein. In the rows showing the Pfam-A domains present in this protein, the different characters represent the output of the HMMscan program. For example, in the first row, the characters (from left to right) indicate the Model used (ls), the domain type identified (PF00051.10), the number of copies of this domain type in this protein (1), the first and last residues of the domain, defined by residue numbering of this protein (25 106), the first and last residues of the HMM of this domain type that align with PF00051 of this protein (1 85), the score of the match (84.6) and the E-value of the match (2.1 e-24). Note that these analyses revealed that the protein is a secreted extracellular protein that contains a secretory signal peptide and two types of extracellular domains. In harmony with the extracellular localization of the protein, it does not contain intracellular signaling domains, nuclear domains or transmembrane helices. However, the protein is erroneous in as much as one of its extracellular protein domains, the Pfam-A domain PF01822 (WSC-domain) is truncated, an error that is detected by MisPred tool 4 (domain-size deviation).