Figure 1.
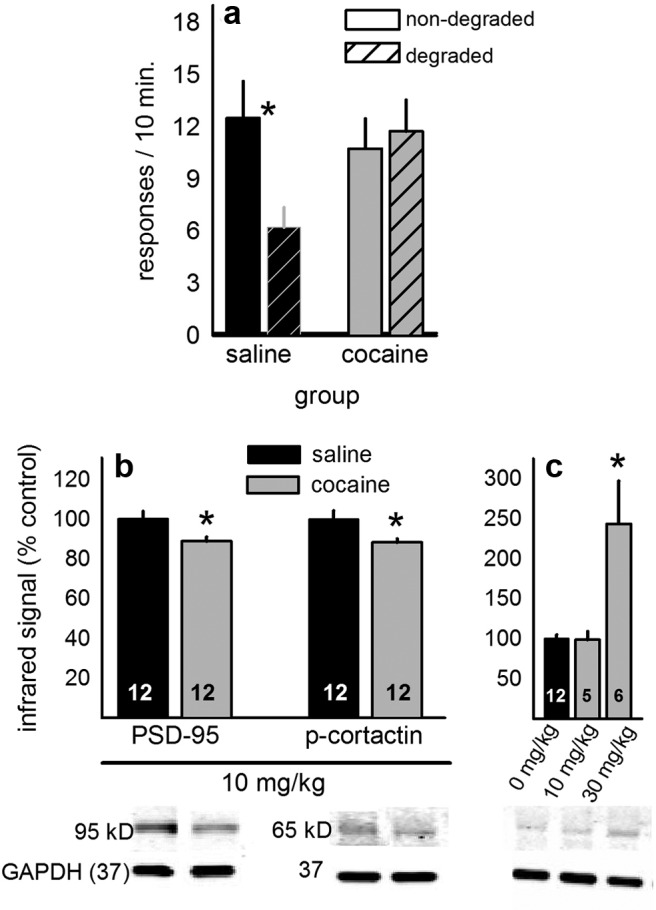
Cocaine diminishes goal sensitivity and DMS PSD95 and cortactin phosphorylation. a, Cocaine exposure immediately after response-outcome contingency degradation disrupted subsequent decision-making, as indicated by nonselective responding on degraded and nondegraded response apertures. b, Acute cocaine also decreased DMS PSD95 and phospho-cortactin. c, The same behaviorally active dose left ventral striatal phospho-cortactin unaffected; only a higher dose increased phosphorylation as previously reported. Bars represent group mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. Representative blots are loaded in the same order as above.
