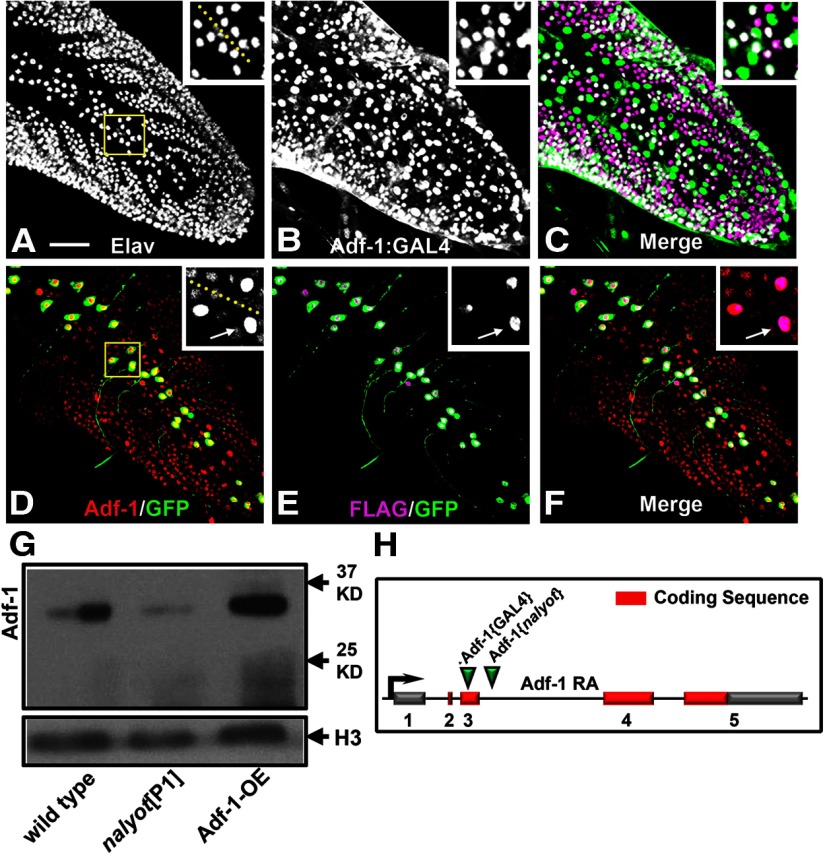
Figure 1.
Adf-1 is expressed in larval motor neurons. A–C, An Adf-1 enhancer trap line (Adf-1-GAL4) expresses β-galactosidase from a UAS-nls-lacZ reporter in larval neurons in the larval nerve cord (B), double-labeled with anti-Elav to mark all postmitotic neuronal nuclei (A). Dorsomedial motor neurons, including RP2 motor neurons, also express Adf-1 (shown in inset and merged images in C). D–F, Overexpression of a FLAG-tagged wild-type Adf-1 using our synthetic GAL4 system is also detectable using staining for the FLAG epitope mCD8::GFP or increased Adf-1 staining. Inset shows a closeup of neuronal nuclei that shows expression of FLAG, GFP, and elevated levels of Adf-1 driven by GAL4. The larval nerve cord is stained for Adf-1 as a reference. Scale bar, 50 μm. G, Western blot of protein extracted from adult brain tissue probed using our peptide antibodies to Adf-1. The previously described nalP1 allele shows reduced expression as expected, while transgenic overexpression of Adf-1 increases Adf-1 protein levels. Anti-Histone H3 is used as a loading control. H–J, Polytene chromosome immunofluorescence shows Adf-1 staining at discrete regions (I). Sytox 24 is used as a general DNA stain to reveal the banding pattern in a standard polytene chromosome preparation (H). K, Schematic of the Adf-1 gene region showing sites of insertion for the pGawB enhancer trap and the P[ry+] nalyot P-element transposons.