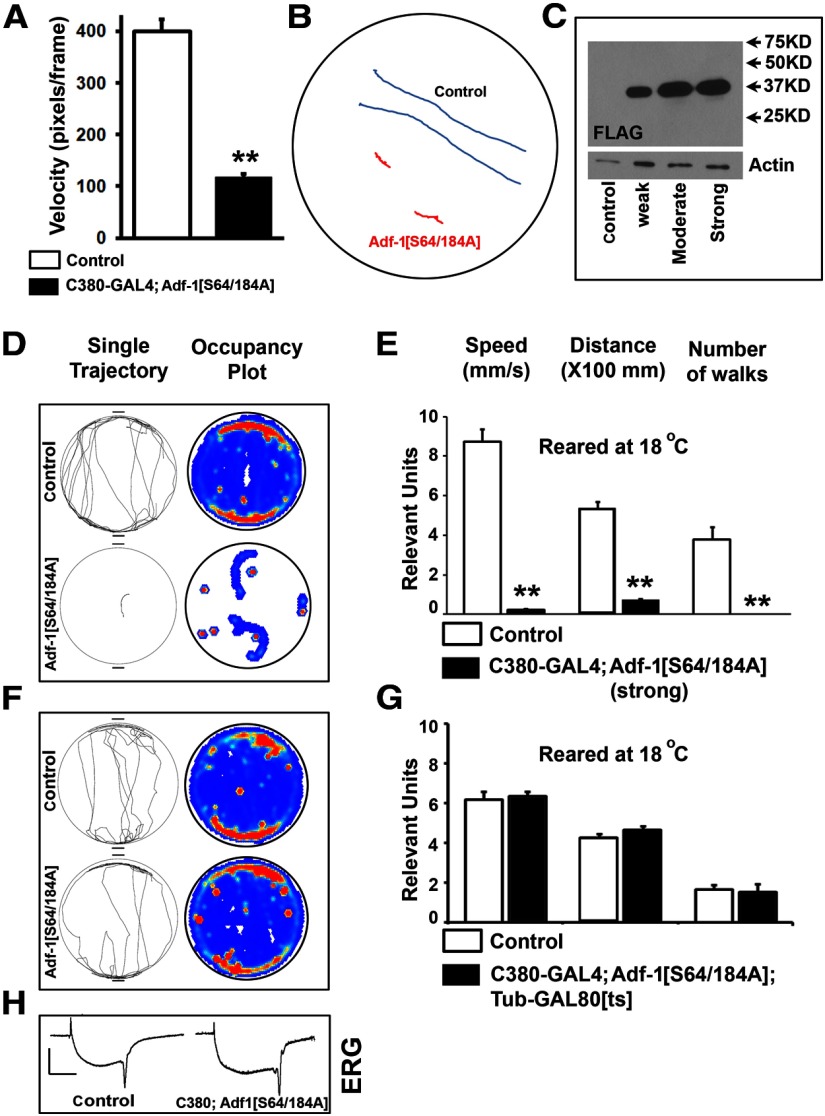
Figure 6.
Behavioral consequences of Adf-1 inhibition in motor neurons. A, Expression of Adf-1[S64/184A] in larval motor neurons using the futschC380-GAL4 driver leads to a dramatic reduction in larval locomotion. Average velocities are reduced by almost fourfold. B, Two representative traces of crawling larvae from control (blue) and Adf-1[S64/184A] animals (red) over a 3 min recording period. C, Western blot of protein from larval brains in which different Adf-1[S64/184A] transgenic lines are used to express FLAG-tagged Adf-1[S64/184A] protein. D, E, Representative individual fly tracks (top) and cumulative occupancy plots of controls compared with animals in which strong expression of Adf-1[S64/184A] is driven from the futschC380-GAL4 driver at 18°C. F, G, The strongly impaired locomotor behavior shown above is dependent on the expression of the transgene and is not observed when a temperature-sensitive GAL80 is used to represses GAL4 activity at 18°C. F, G, Representative individual tracks, cumulative occupancy plots (F), and quantification of locomotor parameters (G). H, Representative electroretinogram traces from control and animals strongly expressing Adf-1[S64/184A] in all neurons. **p < 0.01.