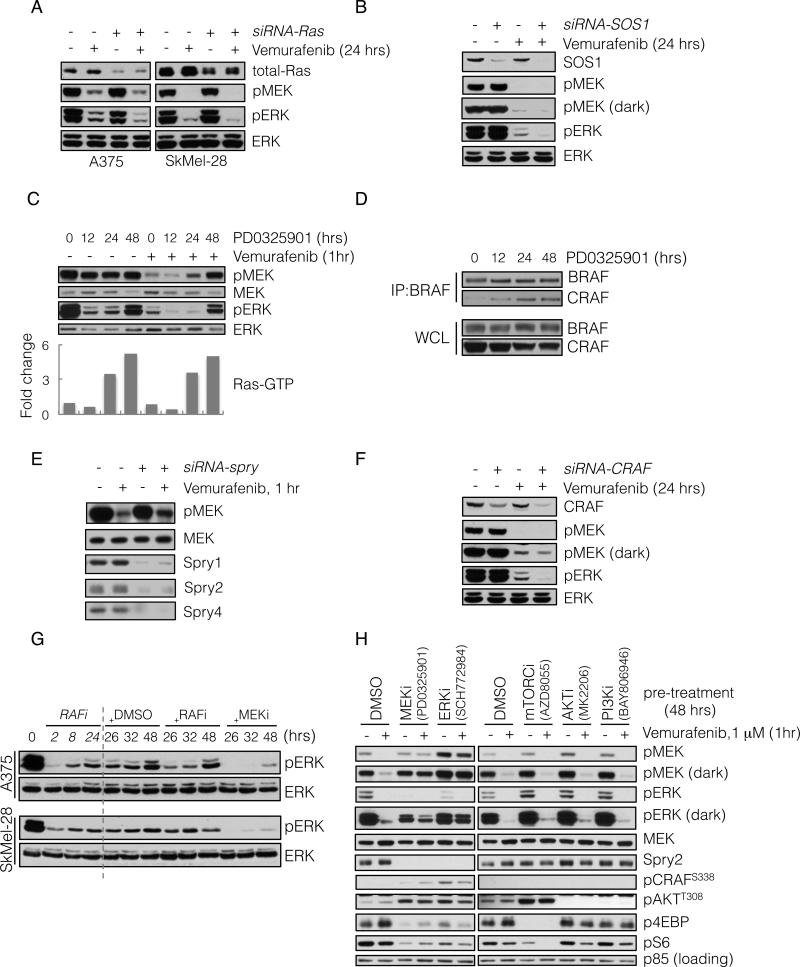
Figure 2. ERK rebound is dependent on formation of CRAF-containing dimers that are resistant to RAF inhibition.
(A) BRAFV600E expressing A375 and SkMel-28 cells were transfected with siRNA pools targeting all three Ras isoforms (+) or scrambled oligonucleotides (-). 48 hours after transfection the cells were treated with vemurafenib (2 μM) for 24 hours and analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) to detect the indicated proteins.
(B) A375 cells were transfected with siRNA pools targeting SOS1. 48 hours after transfection the cells were treated with vemurafenib (2 μM) for 24 hours, and analyzed by IB as above.
(C) A375 cells were untreated or initially pre-treated with MEK inhibitor PD0325901 (50 nM) for the times shown. Subsequently, vemurafenib (1 μM) was added for 1 hour. WCL were assayed to determine changes in pMEK and pERK. WCLs were also analyzed with a GST-RBD Elisa assay. The fold change in the amount of GTP-bound Ras, as compared to untreated cells, is shown.
(D) BRAFV600E expressing Malme-3M cells were treated with PD0325901 (50 nM) for various times. To assess BRAF-CRAF dimerization, WCL were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with a BRAF-specific antibody and then IB for CRAF.
(E) A375 cells were transfected with siRNA pools targeting spry1-4 genes. After 48 hrs they were treated with vemurafenib (1 μM) for 1 hr. WCL were analyzed to determine changes in inhibition of MEK phosphorylation.
(F) A375 cells were transfected with CRAF siRNAs and subsequently treated with vemurafenib for 24 hours. Changes in phospho- and total ERK are shown.
(G) BRAFV600E expressing cell lines were initially treated with vemurafenib (1 μM) for 2, 8 and 24 hours. After 24 hours of treatment, DMSO, vemurafenib (1 μM, RAFi) or PD0325901 (5 nM, MEKi) was added for an additional 2, 8 and 24 hours respectively. The total treatment time is indicated. The effect on ERK signaling is shown.
(H) A375 cells were pre-treated with inhibitors targeting the indicated kinases for 48 hrs, followed by treatment with vemurafenib for 1 hr. WCL were analyzed to detect the ability of vemurafenib to inhibit MEK phosphorylation by RAF, as well as the ability of the indicated compounds to inhibit their targets. Their effects on Spry2 and pCRAF are also shown. See also Figure S2.