Fig. 6.
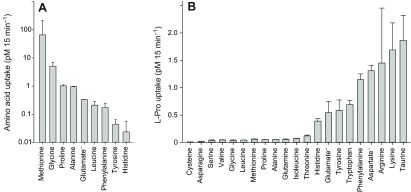
SNF-5-coupled uptake of radiolabeled amino acids. (A) Comparative uptake: 4 days after injection, SNF-5-expressing and uninjected control oocytes from the same batch were bathed in 0.02 μCi ml−1 radiolabeled substrate diluted in 98 mmol l−1 NaCl solution. After 15 min exposure, oocytes were washed in several changes of ice-cold NaCl solution to terminate uptake and were subsequently processed for scintillation counting. Bars represent the mean ± s.e.m. substrate accumulation after pairwise subtraction of disintegrations per minute counted in uninjected oocytes (N>2). (B) Competitive uptake: SNF-5-expressing and uninjected oocytes were exposed to 0.02 μCi ml−1 3H-l-Pro in 98 mmol l−1 NaCl solution containing 5 mmol l−1 unlabeled competing amino acid (2.5 mmol l−1 for Tyr). After 15 min exposure, oocytes were washed and processed for scintillation counting. Bars represent the mean ± s.e.m. uptake of radiolabeled l-Pro under competition with the listed substrates (N>2).
