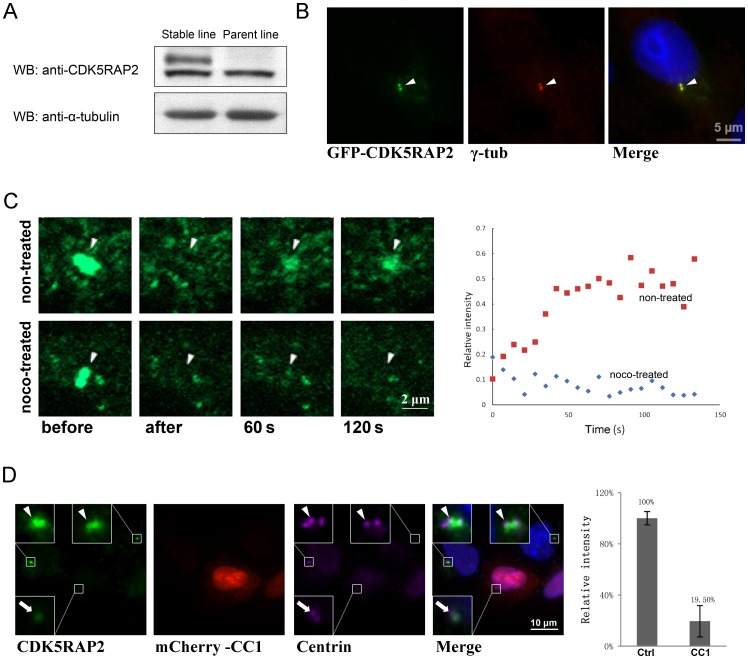
Figure 1. The dynamic recruitment of CDK5RAP2 to centrosomes depends on microtubules and dynein.
(A) Immunoblotting of extracts prepared from MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing GFP-CDK5RAP2. Cells were lysed and extracts were stained with an anti-CDK5RAP2 antibody to detect GFP-CDK5RAP2 and endogenous CDK5RAP2 in either the stable cell line or the parent cell line. Anti-α-tubulin was used as internal control. (B) GFP-CDK5RAP2 is localized on centrosomes. Cells transfected with GFP-CDK5RAP2 were stained with anti-γ-tubulin to label centrosomes. (C) Centrosomal recruitment of CDK5RAP2. FRAP experiments were performed on cells expressing GFP-CDK5RAP2 that were treated with or without nocodazole (noco, nocodazole 10 μM for 1 h) before starting the assays. The intensity of the CDK5RAP2 signal relative to its original level (before bleaching) on centrosomes (arrowheads) is plotted on the right; the intensity recovered to 60% of the original intensity (n = 5). (D) Effect of the disruption of dynein-dynactin on the centrosomal accumulation of CDK5RAP2. The centrosomal level of CDK5RAP2 was determined in cells un-transfected and transfected with mCherry-CC1; relative amounts of centrosomal CDK5RAP2 are shown on the right (n≥30 cells for each case; error bars, S.D. p<0.001). Arrows and arrowheads point to centrosomes in CC1-positive and CC1-negative cells. Centrin serves as an indicator of centrosomes. Centrosomes are magnified in insets. Scale bar, 10 μm. Representative results of at least three separate experiments are shown here.