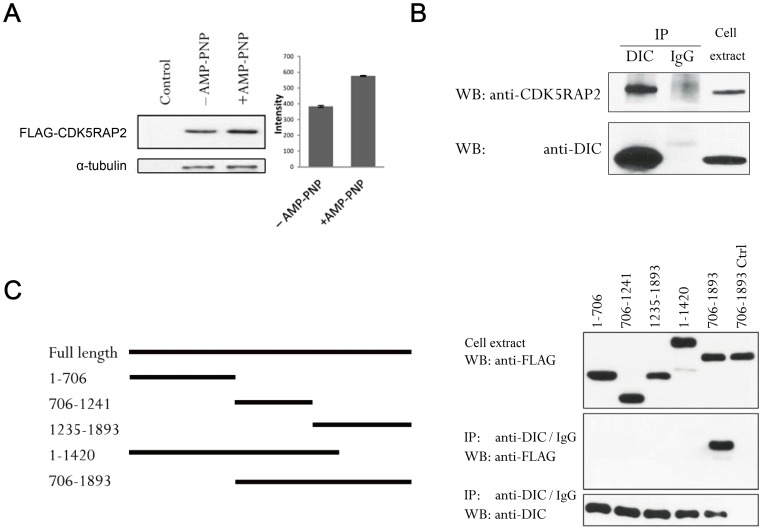
Figure 2. CDK5RAP2 associates with dynein.
(A) Extracts of HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-CDK5RAP2 were incubated with taxol-polymerized microtubules in the absence or presence of AMP-PNP; control samples lacked polymerized microtubules. After incubation, microtubules were spun down through a sucrose cushion and the pellets were immunoblotted with an anti-FLAG antibody for CDK5RAP2; α-tubulin in these pellets was quantified by staining with anti-α-tubulin antibody (n = 3, p<0.001). (B) DIC was immunoprecipitated from HEK293T extracts using an anti-DIC antibody, normal mouse IgG served as a control. The immunoprecipitates (“IP” here and in other figures) and cell extracts were probed for DIC and CDK5RAP2 by Western blotting (“WB” here and in other figures). (C) Mapping the DIC-binding region in CDK5RAP2. Anti-DIC immunoprecipitation was performed on HEK293T ectopically expressing CDK5RAP2 fragments. Immunoprecipitates and cell extracts were analyzed for DIC and for the CDK5RAP2 fragments with anti-FLAG. A control immunoprecipitation (Ctrl) was performed using normal mouse IgG on lysates of 706–1893-expressing cells.