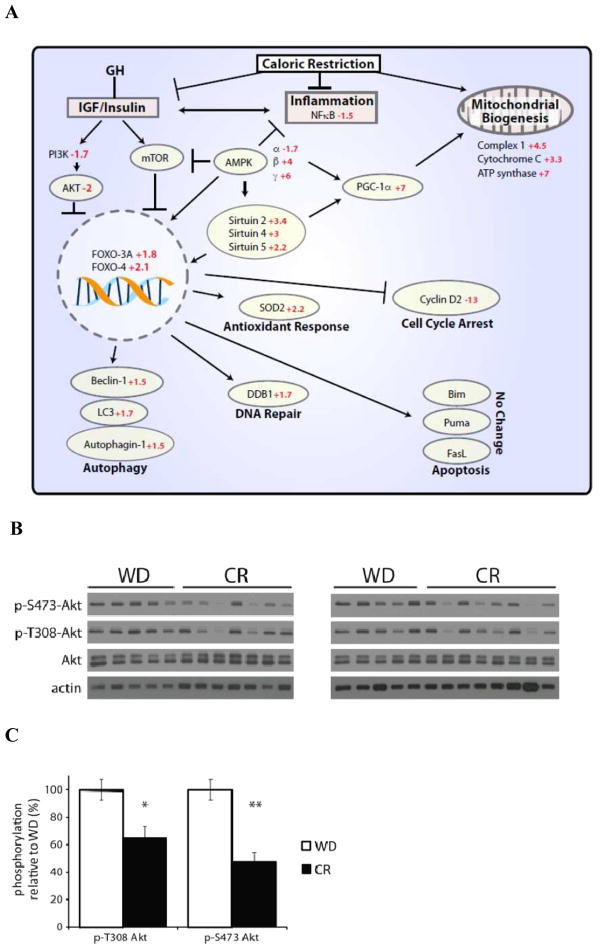
Fig. 2. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional modifications of the PI3K/AKT/FOXO pathway in human skeletal muscle by CR.
(A) Transcriptional down-regulation of the PI3K/AKT/FOXO signaling pathway by CR. GH: growth hormone; IGF: insulin-like growth factor; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: protein kinase B (PKB); FOXO-3A: forkhead box O3; FOXO-4: forkhead box O4; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; LC3: microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; NFκB: nuclear factor-kappaB; SOD2: superoxide dismutase 2; DDB1: damage-specific DNA binding protein 1; FASL: fas ligand.
Western blot of human skeletal muscle from individuals on a Western diet (WD) or caloric restricted (CR) diet. Immunoblot (B) and quantification (C) of western blots in panel a for p-T308 AKT and p-S473 AKT was performed using NIH ImageJ, and normalized to total AKT expression. (*p<0.01, **P<0.00003 (n=10 WD, 15 CR samples)). Bars indicate mean ± SEM.