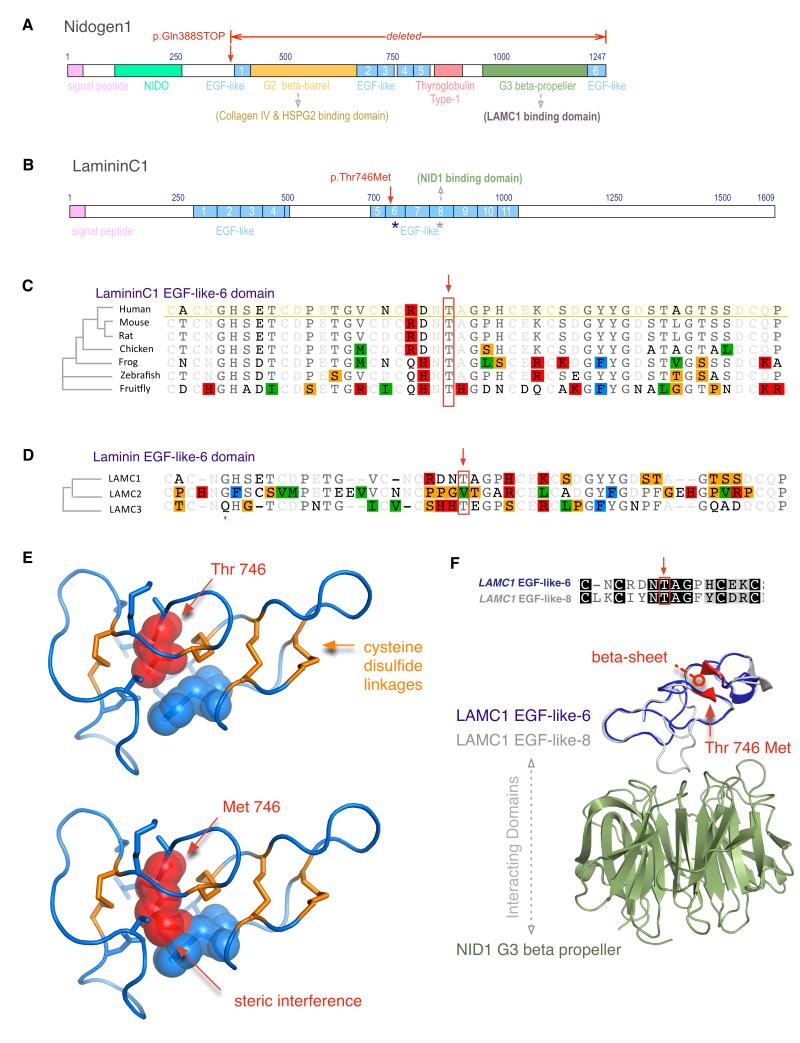
Figure 2. Protein Domain and Structure analysis.
a. Nidogen1 domains. A stop codon leads to deletion of the Nidogen1 G2 beta barrel domain (green), several EGF-like domains (blue), and the thyroglobulin Type-1 domain.
b. LamininC1 domains. The family-2 mutation was found in EGF-6-like (blue asterisk). There are 11 EGF-like domains (blue), and a previously known interaction with Nidogen-1 occurs through EGF-8-like domain (grey asterisk).
c. Ortholog alignment shows high evolutionary conservation of the Threonine-746 residue (red box).
d. Paralog alignment of three human EGF-6-like domains from LAMC1, C2, and C3 shows size conservation of the 746-residue, Threonine (M.W. 119 Da) and Valine (M.W. 117 Da, red box).
e. The normal threonine-746 (red) occupies a small space between rigid cysteine disulfide bridges (orange), and a mutation to methionine leads to steric interference with surrounding residues (blue).
f. EGF-like-6 domain (homology model in blue) shows 33% sequence identity to EGF-like-8 domain (grey), which interacts with the Nidogen1 G2 beta barrel domain (green). The mutation is expected to disrupt a beta sheet (red).