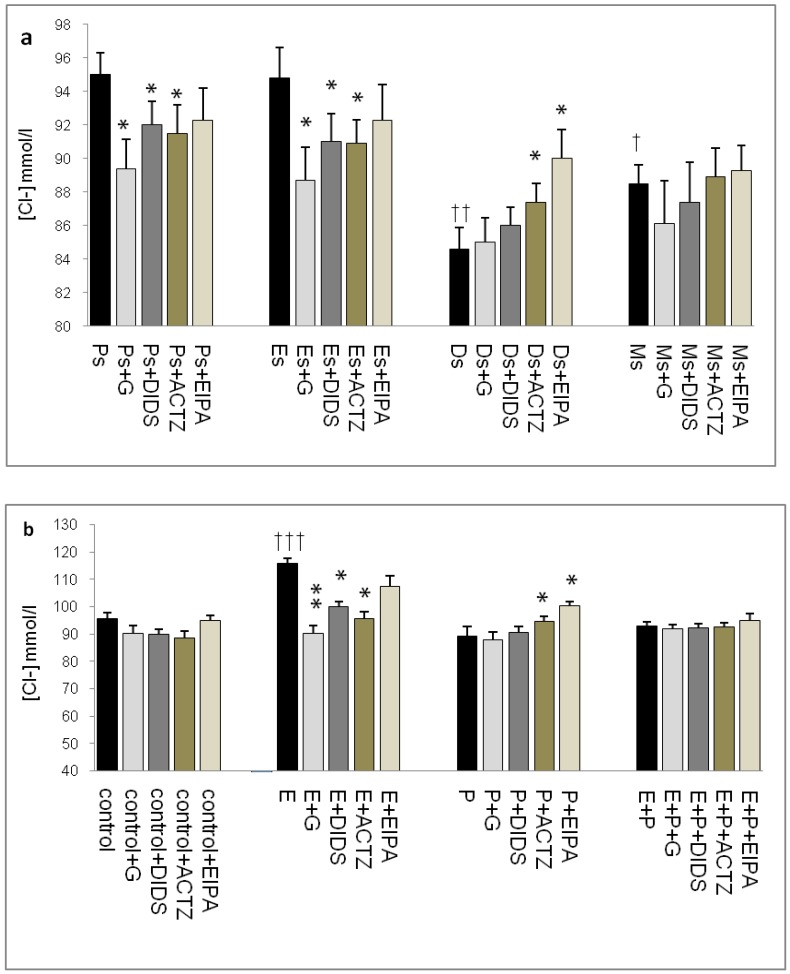
Fig 4.
Uterine fluid Cl- concentrations with and without the presence of protein/enzyme inhibitors in (a) rats at different stages of the oestrous cycle and (b) ovariectomized rats receiving steroid replacement. The highest Cl- level was observed under E influence. Glibenclamide and ACTZ administration caused a decrease in Cl- concentration in rats at Es, Ps and following E treatment. Meanwhile, Cl- concentration was reduced under P influence. ACTZ and EIPA administration caused an increase in Cl- concentration at Ds and following P treatment. E: 0.2µg 17β-oestradiol, P: 4mg progesterone, E+P: 0.2 µg 17β-oestradiol + 4mg progesterone. Ps: proestrus, Es: estrus, Ms: metestrus, Ds: diestrus. G: glibenclamide, ACTZ: acetazolamide, DIDS: 4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid disodium salt hydrate and EIPA: 5-(N-Ethyl-N-isopropyl)-amiloride † as compared to Es or control, * as compared with the group without inhibitor. (*:p<0.05), (**:p<0.01), (***p<0.001). n= 6 per group. One way ANOVA and Tukey's test were used to analyze the results which were presented as mean ± SEM.