Figure 2.
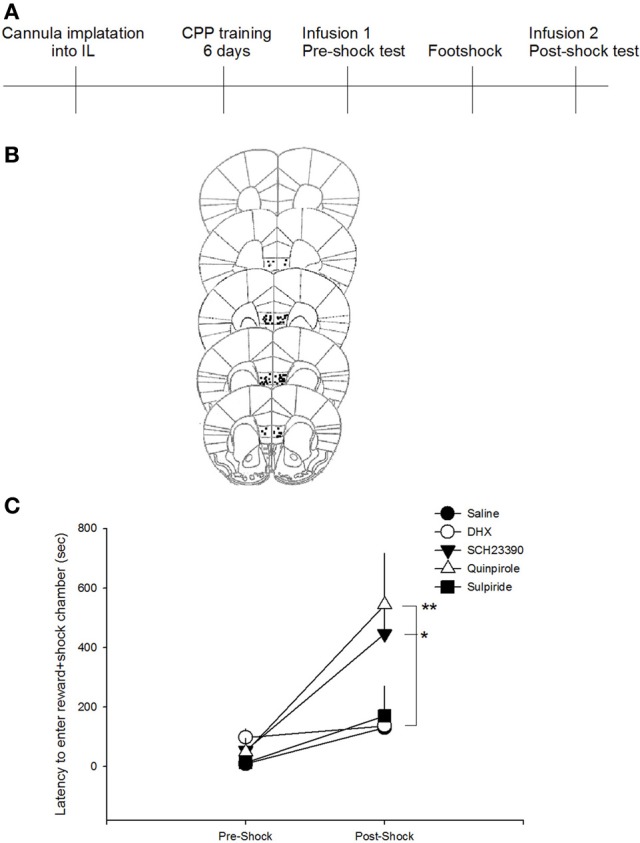
D1 antagonism or D2 agonism reduce compulsive-like reward seeking. (A) Experimental timeline. Mice received infusions of drugs into the IL only during test sessions to ensure that effects were on the expression, not acquisition, of compulsive-like behavior. (B) Only mice whose cannula could be confirmed to be within the IL were included in behavioral analyses. Images modified from Paxinos and Franklin (2001). (C) Antagonism of the D1 receptor with SCH23390 or agonism of the D2 receptor with quinpirole in the IL reduced compulsive-like reward seeking as indicated by an increase in latency to enter the reward-paired chamber only after pairing with foot shock (adverse consequence). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
