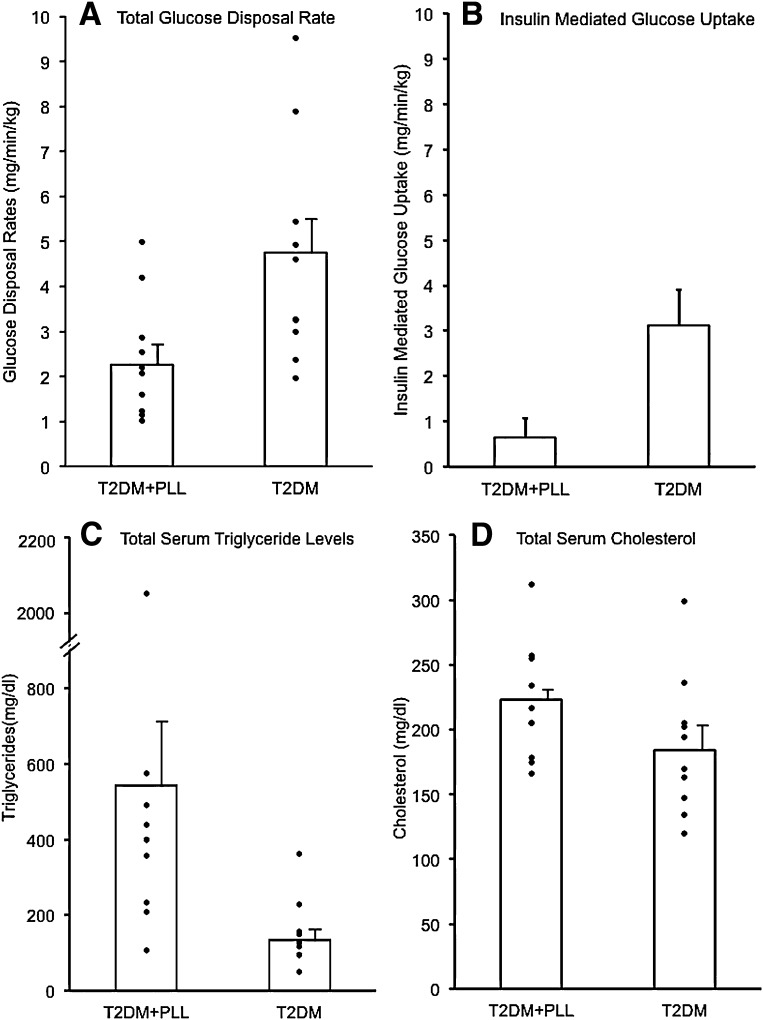
Figure 2.
Comparison of GDR and total triglycerides and cholesterol. A: GDRs were assessed using the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp technique and normalized per kilogram of body weight. Mean ± SE values were significantly lower in 10 patients with T2DM and PLL (T2DM+PLL) compared with 10 patients with common T2DM (2.26 ± 0.42 vs. 4.74 ± 0.77 mg/min/kg; P < 0.05). B: In each subject, the value for non-insulin–mediated glucose disposal (1.6 mg/min/kg; see Insulin resistance: GDRs and fasting insulin levels) was subtracted from the total GDR during the clamp to obtain the insulin-mediated GDR. The mean ± SE value for insulin mediated glucose uptake in T2DM+PLL was minimal and markedly reduced compared with common T2DM (0.64 ± 0.42 vs. 3.12 ± 0.77 mg/min/kg; P < 0.05). C: The mean ± SE value for triglycerides was increased in 10 patients with T2DM and PLL (T2DM+PLL) compared with 10 patients with common T2DM (543 ± 175 vs. 134 ± 28 mg/dL; P < 0.05). D: Mean ± SE levels of total cholesterol were statistically similar in comparing the T2DM groups with and without PLL (223 ± 14 vs. 184 ± 17 mg/dL; P = 0.10). Data in all panels were controlled for BMI, age, and race.