Fig. 4.
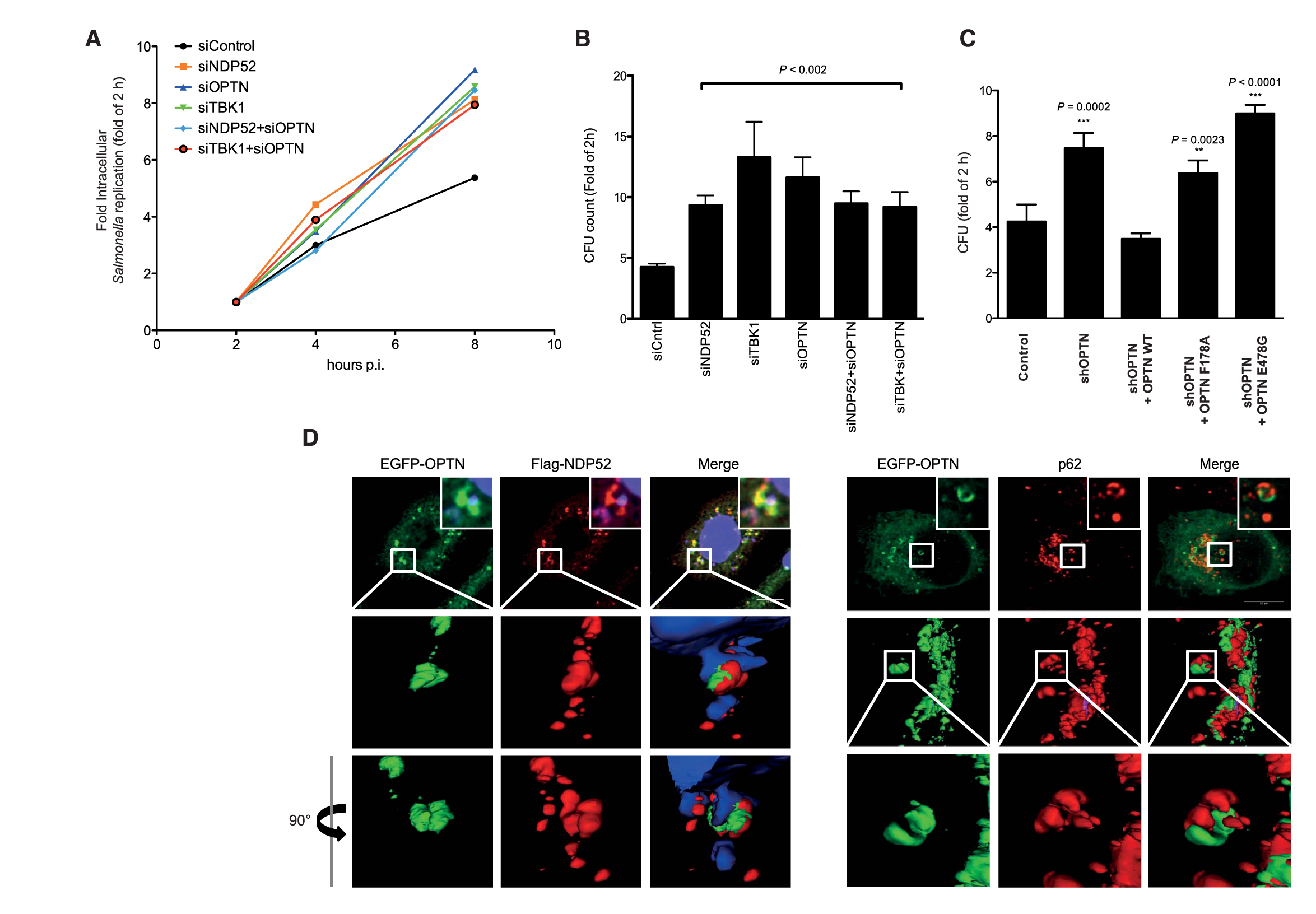
Salmonella proliferation is enhanced in the absence of OPTN in vivo. (A) HeLa cells transfected with indicated siRNAs were infected with Salmonella (SL1344) and lysed at the indicated time points post-infection, and bacterial colonies were counted on selective agar plates. (B) Numbers of bacteria recovered from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and infected with Salmonella for 8 hpi. Intracellular Salmonella replication was calculated as fold increase at the 2-hour time point. Depletion of OPTN, NDP52, or TBK1 resulted in increased Salmonella intracellular replication. Error bars indicate mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.002, two-tailed t test. CFU, colony-forming units. (C) ShRNA OPTN-depleted HeLa cells were transiently reconstituted with shRNA-resistant OPTN WT, shR-OPTN F178A, and shR-OPTN E478G. Both LIR mutants and Ub-binding mutants of OPTN failed to rescue OPTN-depleted HeLa cells 8 hpi compared with OPTN WT. Error bars indicate mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. (D) Three-dimensional reconstitution of confocal image z-stacks of Salmonella-infected HeLa cells at 4 hpi. EGFP-OPTN WT (green), NDP52 (red, left panel), and endogenous p62 (red right panel) form distinct “patches” on the surface of cytosolic Salmonella.