Figure 2.
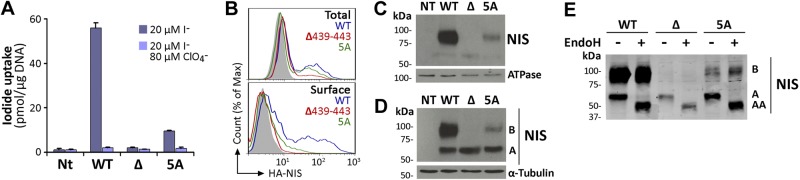
Insertion of 5 Ala partially rescues NIS plasma membrane targeting. A) Steady-state I− uptake in nontransfected (NT), and permanently expressing WT, Δ439–443 (Δ), or 5A NIS MDCK-II cells. Cells were incubated with 20 μM I− in the absence (dark bars) or presence (light bars) of 80 μM ClO4−. Results are expressed as means ± sd (pmol I−/μg DNA). Values are representative of ≥3 different experiments; in each experiment activity was analyzed in triplicate. B) Representative FACS analysis of NIS expression under permeabilized (top panel, total) and nonpermeabilized (bottom panel, surface) conditions. Cells were stained with anti-HA Ab, followed by R-phycoerythrin-conjugated anti-rat Ab. Nontransfected cells are represented in solid gray; WT NIS in blue line; Δ439–443 NIS in red line, and 5A NIS in green line. C) Immunoblot analysis of cell surface-biotinylated proteins from nontransfected and WT, Δ439–443, or 5A NIS-expressing MDCK-II cells, performed with anti-human NIS Ab (top panel). The plasma membrane marker Na+/K+ ATPase was used as a positive control (bottom panel). D) Immunoblot analysis of membrane fractions from WT, Δ439–443, or 5A NIS-transfected MDCK-II cells performed with anti-human NIS Ab (upper panel). The NIS electrophoretic pattern includes immaturely glycosylated (∼60 kDa, band A), and mature or fully glycosylated (∼100 kDa, band B) polypeptides. The housekeeping protein α-tubulin was used as loading control (bottom panel). E) Immunoblot analysis of membrane proteins treated (+) or not (−) with Endo H, and immunoblotted with anti-human NIS Ab. Right side of the blot indicates the relative electrophoretic mobilities of the corresponding NIS polypeptides (AA: ∼50, A: ∼60, B: ∼100 kDa), depending on glycosylation status.
