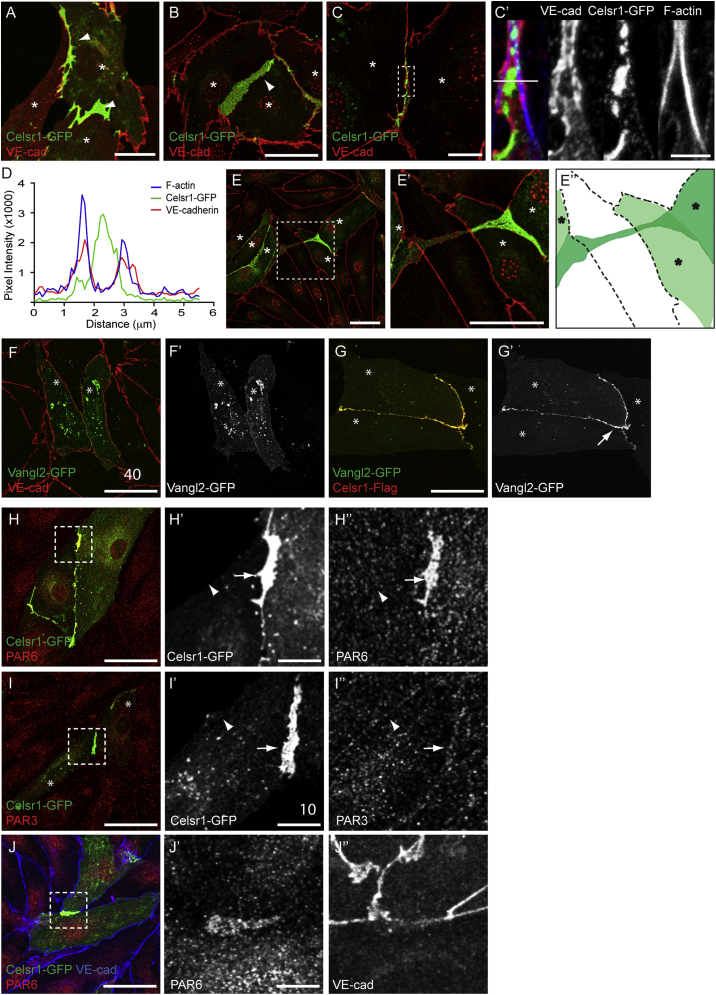
Figure 5.
Celsr1 Localizes to Specific Membrane Domains within Cellular Protrusions in Primary Lymphatic Endothelial Cells
(A–E′) Celsr1-GFP (green) and VE-cadherin (red) localization during the establishment (A and B) and maturation (C) of cell-cell junctions. Note mutually exclusive localization of Celsr1-GFP and VE-cadherin/F-actin to specific membrane domains (C′). Single channel images for Celsr1-GFP, VE-Cadherin, and F-actin are included as indicated. (E and E′) show a Celsr1-GFP positive cell making contact to a distant Celsr1 positive cell underneath another cell. (E″) shows schematic representation of cell arrangement. Asterisks indicate cells expressing Celsr1-GFP. (D) Intensity scan profile showing pixel intensity values for Celsr1-GFP (green), VE-cadherin (red), and F-actin (blue) measured across a cell-cell junction. The position of the scan line is shown in (C′).
(F–G′) Localization of Vangl2-GFP (green) with endogenous VE-cadherin (red, F) or Celsr1-Flag (red, G). Note the recruitment of Vangl2-GFP to cell-cell contacts only in presence of Celsr1-Flag (arrow in G′).
(H–J″) PAR6 and PAR3 localization in Celsr1-GFP expressing cells. Single channel images of the boxed areas are shown. Note the specific recruitment of PAR6 to Celsr1 positive (arrow in H′ and H″) but not negative (arrowhead in H′ and H″) junctions whereas weak PAR3 signal is observed at both junctions (arrow and arrowhead in I′ and I″). PAR6 is recruited to Celsr1 positive junctions before the arrival of VE-cadherin (J–J″).
Scale bars represent 40 μm (A–C, E–G′, H, I, and J), 10 μm (C, H′, H″, I′, I″, J′, and J″), and 2.5 μm (C′).
See also Figures S4–S6 and Movies S2, S3, and S4.