Figure 6.
Celsr1 Regulates Lymphatic Endothelial Adherens Junctions
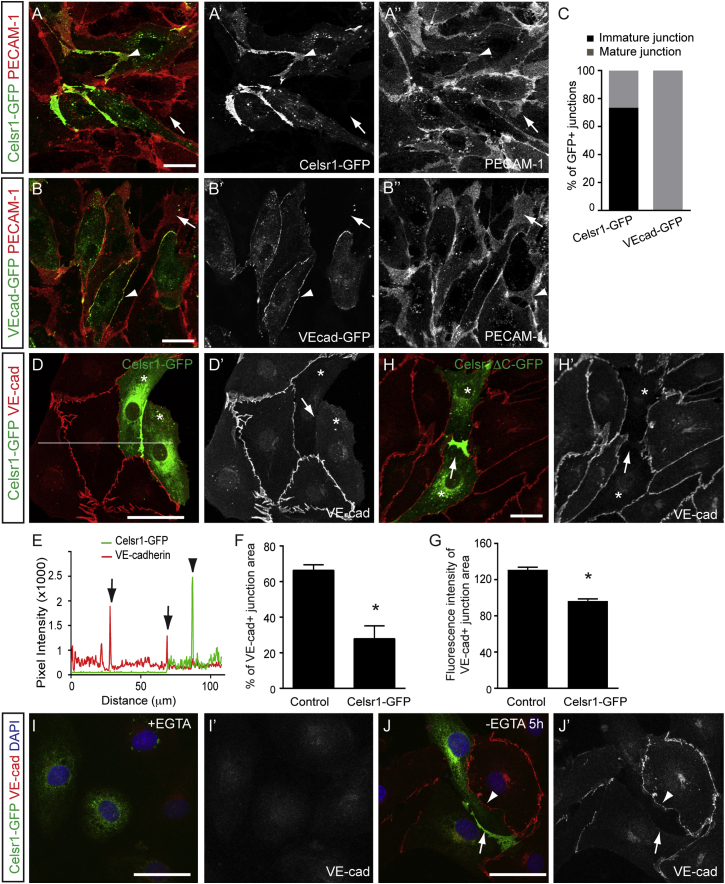
(A–B″) Localization of Celsr1-GFP (A, arrowhead) and VE-cadherin-GFP (B, arrowhead) in the LECs, costained for PECAM-1. Single channel images are shown on the right. Note the presence of membrane protrusions (arrows) except in the VE-cadherin-GFP-positive junctions.
(C) Quantification of VE-cadherin-GFP and Celsr1-GFP positive cell contacts (n = 174 junctions for Celsr1-GFP and n = 88 for VE-cad-GFP) showing protrusions (immature) or linear junctions (mature).
(D and D′) VE-cadherin immunostaining in Celsr1-GFP expressing cells. Note the reduction of VE-cadherin at the junction in between two Celsr1-GFP expressing cells (arrows) compared to control cells.
(E) Intensity scan profile showing pixel intensity values for Celsr1-GFP (green) and VE-cadherin (red) measured across cell junctions. The position of the scan line is shown in (D).
(F) VE-cadherin positive junction area measured at overlapping membrane contacts in control and Celsr1-GFP positive junctions. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3 experiments) ∗p < 0.0001 (Student’s t test).
(G) VE-cadherin levels, measured as fluorescence intensity of VE-cadherin positive area, in control and Celsr1-GFP positive junctions. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 63 junctions) of a representative experiment of three independent experiments ∗p < 0.0001 (Student’s t test).
(H and H′) VE-cadherin immunostaining in Celsr1ΔC-GFP expressing cells showing reduction of VE-cadherin at the Celsr1-positive junction (arrow) compared to control cells.
(I–J′) VE-cadherin (red) and DAPI (blue) staining in Celsr1-GFP (green) expressing cells in the presence (I) or 5 hr after the removal of EGTA (J). Note reduced VE-cadherin recruitment to a Celsr1 positive (arrow) when compared to a Celsr1 negative junction (arrowhead in J′).
Scales bars represent 40 μm.
See also Figure S7.