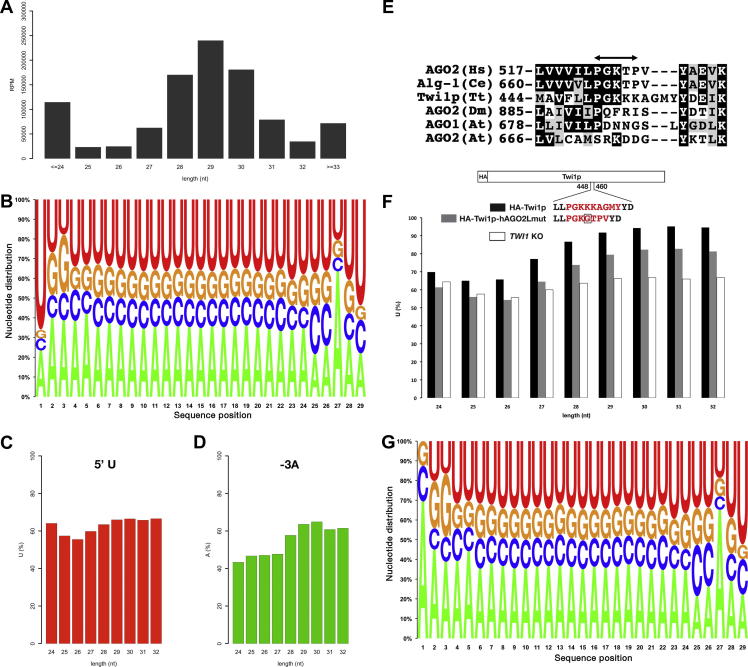
Fig. 2.
Analyses of unloaded scnRNAs and the nucleotide specificity loop. (A) Size distribution of the small RNAs from the TWI1 KO cells. The number of sequenced RNAs (reads per million sequences (RPM)) of each size is shown. (B) Base composition of the 29-nt RNAs. (C) Fraction of the RNAs with uracil as the first base (5′ U). (D) Fraction of the RNAs with adenine as the third base from the 3′ end (-3A). (E) Comparison of the nucleotide specificity loops of the different Argonaute proteins. The region corresponding to the proposed nucleotide specificity loop [27] of human AGO2 is marked with a double-headed arrow. Human (Hs) AGO2 and C. elegans (Ce) Alg-1, which tend to bind to 5′ U/A RNAs, share a conserved sequence in the loop. Tt: Tetrahymena thermophila; Dm: Drosophila melanogaster; At: Arabidopsis thaliana. (F) Fraction of the 5′ U RNAs in HA-Twi1p-associated (black), HA-Twi1p-hAGO2Lmut-associated (gray), or total TWI1 KO (white, same data as (C)) small RNAs. The replaced nucleotide specificity loop region is shown in red. The extra glycine inserted into the nucleotide specificity loop of human AGO2 is marked with a square. (G) Base composition of the non-5′ U 29-nt RNAs from the TWI1 KO cells. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)