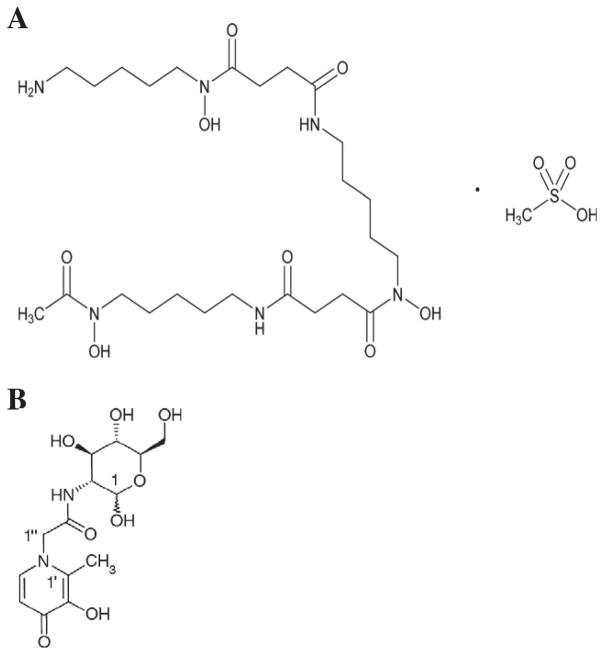
Fig. 1.
Structures of desferrioxamine and Feralex-G. (A): DFO: deferrioxamine mesylate (USAN); alternatively desferrioxamine mesilate (BAN). DFO is a commercially available siderophore (molecule that sequesters iron from the environment) produced by Streptomyces pilosus. It is a hexadentate chelator, and binds trivalent iron or aluminum in a 1:1 ratio. It is used in many countries in the mesylate form to treat various forms of iron overload, and also aluminum overload. A major drawback to its use is that it is effective only when administered parenterally [65]. Image kindly provided by Andrzej Wilk, PhD, Senior Scientific Liaison, US Pharmacopeia; CAS Number 138–14-7; DFO has a molecular formula of C25H48N6O8·CH4O3S; MW 657. (B): Feralex-G. Feralex-G is an experimental oral chelator made from three natural substances—glucosamine (1), an amino acid, glycine (1″) and maltol (1′) [76]. It was designed to enter cells via complexing of the glucosamine “tail” with glucose transporters, and to be a safe replacement for DFO which is effective only parenterally (i.e., by intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intravenous routes). Feralex-G is bidentate and complexes with trivalent metal ions in the ratio of 3:1. Hydrophilicity of Feralex can be altered by substitution of the amino acid linker. Image reproduced from Kruck et al. [61] with permission. Feralex-G has a molecular formula of C13H13N2O7; MW 344 [61,62,76].