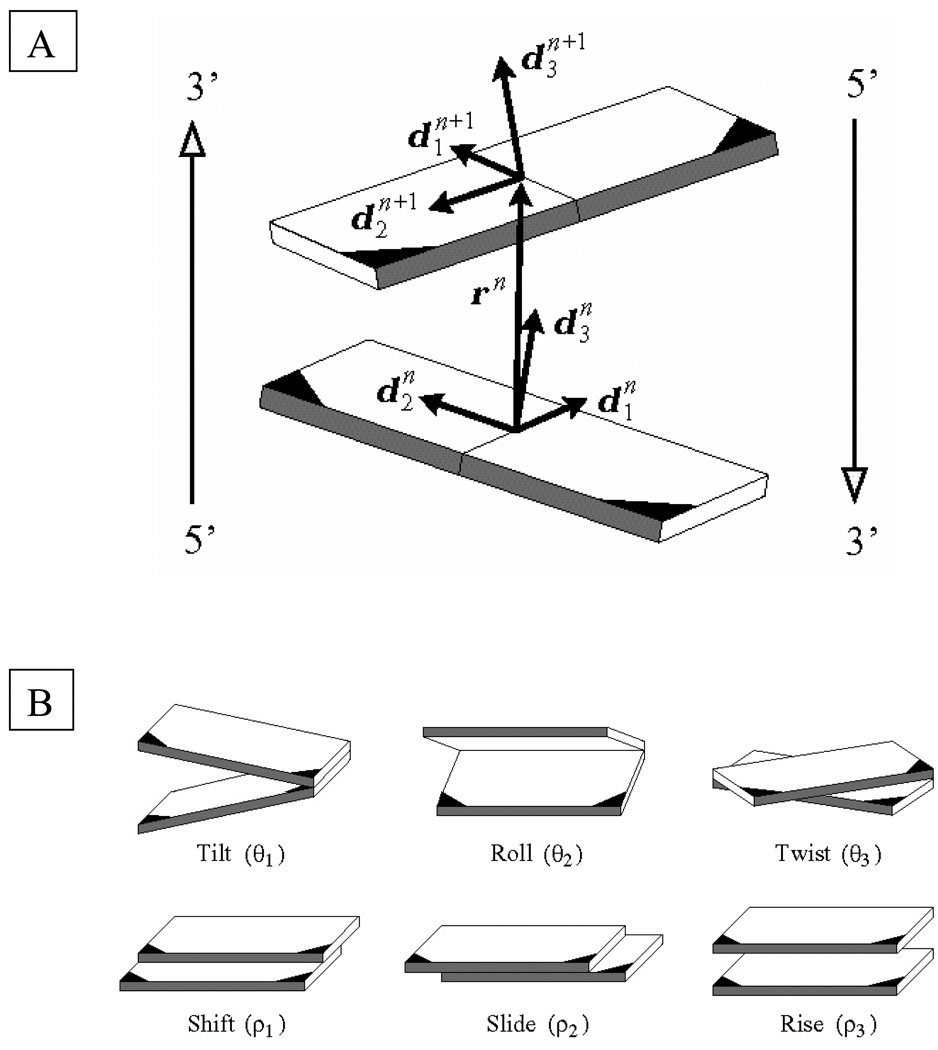
Fig. 1.
(A) Model of a base-pair step showing the vector rn = xn+1 − xn that connects the origins of successive residues and the orthonormal frames on the base pairs. Each base is covalently bonded at the darkened corner to one of the two sugar-phosphate chains. The minor-groove edges of base pairs are shaded in gray, and the antiparallel 5′-3′ directions of the complementary strands are denoted by the arrows at the edges.
(B) Schematic representation of kinematical variables describing the relative orientation and displacement of base pairs in a step. Images illustrate positive values of the designated variables with respect to the leading strand, denoted in (A) by the arrow on the left.