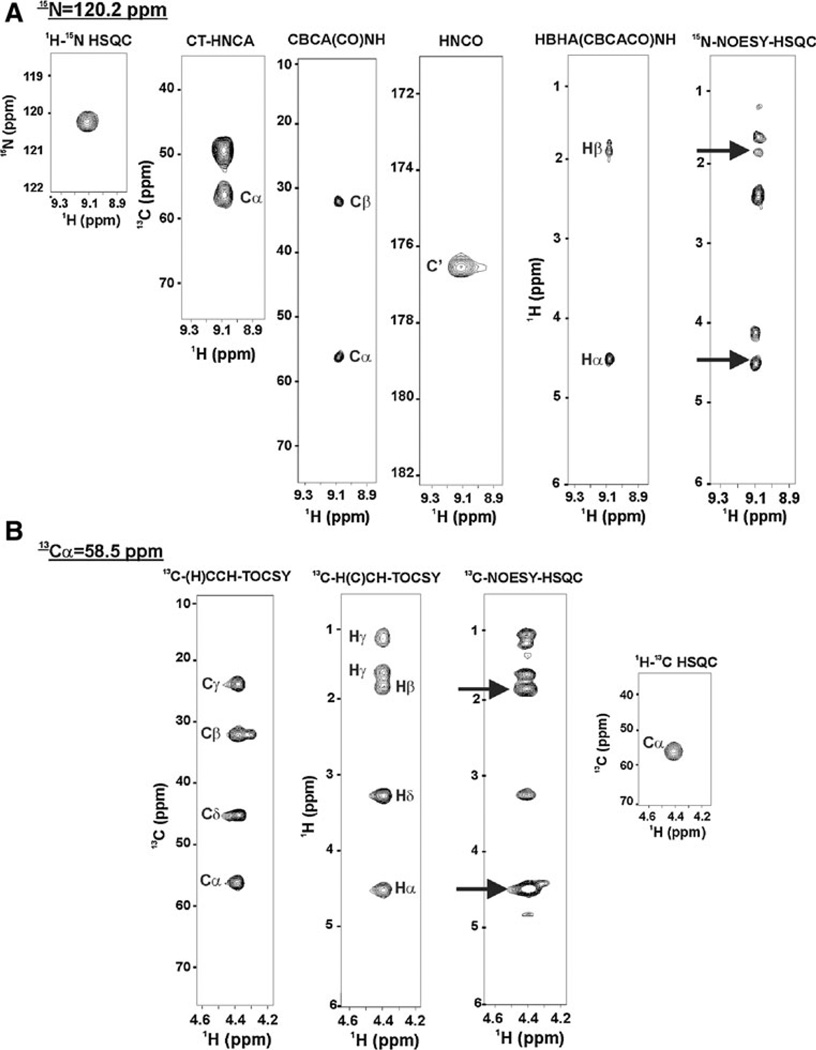
Fig. 4.
Summary of the algorithm used by FMCGUI and ABACUS to define spin systems and sequential connectivities based on peak lists from the minimal dataset. The procedure begins by identifying spins for the PB fragment highlighted in Fig. 1: in (a) The 15N-1H HSQC is used as a reference spectrum to define the 1H-15N correlation for the aspartate residue, the CBCACONH and HNCA identify Cα and Cβ for the arginine, the HNCO is used to define C’ for later use in TALOS and to identify overlapping spin systems. The HBHA(CBCACO)NH confirms the Hα and Hβ in the 15N-edited NOESY (arrows identify through-space NOE correlations of protons). In (b) Complementary (H)CCH-TOCSY and H(C)CH-TOCSY experiments allow for facile assignment of side chain resonances beyond β carbon that can be easily mapped to the corresponding strip in the 13C-edited NOESY and correlation peak in the constant time 1H-13C HSQC. Peak lists are generated for these experiments and are loaded into FMCGUI for implementation of the FAWN and/or ABACUS protocols