Figure 2. Characterization of patient- and mouse model-derived exosomes.
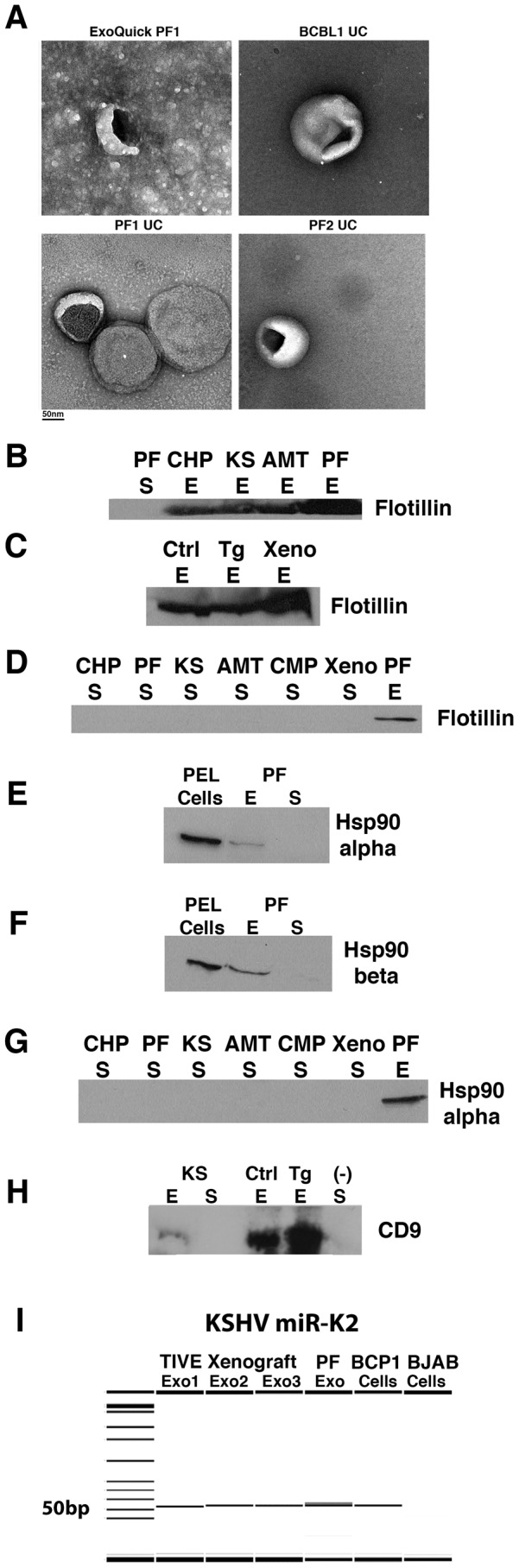
(A) EM images of exosomes prepared from patient and tissue culture samples using Exoquick and ultracentrifugation (UC) methods. PF1, pleural fluid patient 1; PF2, pleural fluid patient 2; BCBL1 – PEL cell line. Scalebar is shown below images. (B–H) Abbreviations are as follows: CHP – Control, KSHV(−) Human Plasma, AMT – patients with non-KS AIDS malignancies, KS – Kaposi's Sarcoma patients, PF – Primary PEL Pleural Fluid, Ctrl – Control Mouse Serum, Tg – KSHV Latency Locus Transgenic Mouse Model, Xeno – TIVE-KSHV Xenograft Mouse Model, (−) KSHV-negative BJAB cell line. The exosomal markers flotillin-2 (B,C), Hsp90 alpha (E,G), Hsp90 beta (F) and CD9 (H) were analyzed by Western blot in human and mouse exosomes (abbreviated E) isolated using the Exoquick method. Exosome-depleted supernatants (abbreviated S) were also analyzed for the presence of Flotillin (B,D) and Hsp90 alpha (E,G). CD9 was detected in mouse exosome samples and exosomes from KS patients (KS), confirming our method of exosome isolation (H). As expected, the exosomal marker was absent in the supernatant fraction and in our negative control BJAB exosome-depleted supernatant fraction. Flotillin was present in exosomes derived from control (Ctrl), transgenic (Tg) and xenograft (Xeno) mouse models but was not present in the supernatant fraction. Hsp90 alpha and beta were expressed in PEL cells (VG1, a KSHV+ PEL cell line) and pleural fluid-derived exosomes (PF) but not in the supernatant. (I) KSHV miR-K2 expression was determined by qPCR and products were run on the Caliper LabChip GX. BCP1-KSHV (+) PEL cell line, Exo – RNA from exosome fraction, Cells – RNA from cell pellet. Exo1,2 and 3 denote three individual TIVE xenograft mice.
