Figure 3. Excision of ICEBs1 from secondary attachment sites.
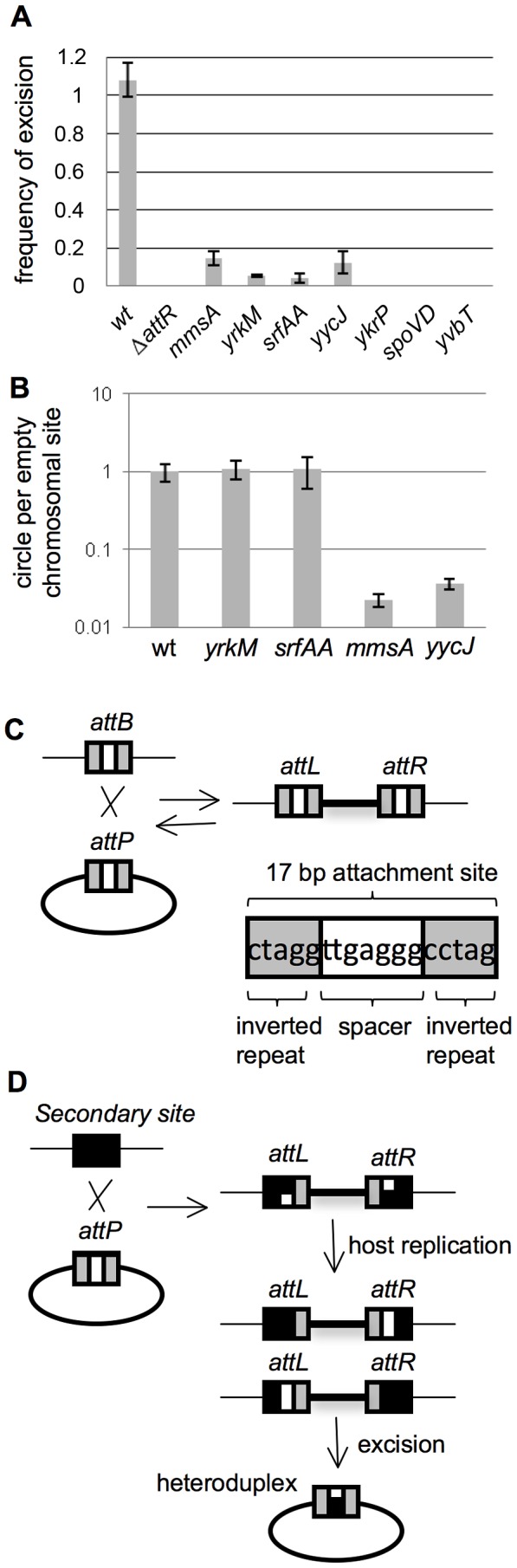
A–B. Excision frequencies and relative amounts of the excision products (circular ICEBs1 and empty chromosomal site) were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were grown in defined minimal medium with arabinose as carbon source. Products from excision were determined two hours after addition of xylose to induce expression of Pxyl-rapI to cause induction of ICEBs1 gene expression. Primers for qPCR were unique to each attachment site. Strains used include: wt, that is, ICEBs1 inserted in attB (CAL874); ΔattR, ICEBs1 integrated in attB, but with the right attachment site deleted and ICEBs1 unable to excise (Figure 1) (CAL872); mmsA::ICEBs1 (KM70); yrkM::ICEBs1 (KM72); srfAA::ICEBs1 (KM141); yycJ::ICEBs1 (KM132); ykrP::ICEBs1 (KM77); spoVD::ICEBs1 (KM130); yvbT::ICEBs1 (KM94). Each strain was assayed at least three times (biological replicates) and qPCR was done in triplicate on each sample. Error bars represent standard deviation. A. Frequency of excision of ICEBs1 from the indicated site of integration. The relative amount of the empty chromosomal attachment site was determined and normalized to the chromosomal gene cotF. Data were also normalized to a strain with no ICEBs1 (JMA222), which represents 100% excision. B. Relative amount of circular ICEBs1 compared to the amount of empty chromosomal attachment site for the indicated insertions. The relative amount of the ICEBs1 circle, normalized to cotF, was divided by the relative amount of the empty attachment site, also normalized to cotF. These ratios were then normalized to those for wild type. C. Cartoon of integration of ICEBs1 into its primary bacterial attachment site attB. attB is identical to the attachment site on ICEBs1, attICEBs1. They consist of a 17 bp region with 5 bp inverted repeats (gray boxes) on each side of a 7 bp spacer region (white box). During integration and excision, a recombination event occurs in the 7 bp spacer (crossover) region [38]. D. Cartoon of integration of ICEBs1 into secondary integration sites. A secondary integration site is indicated with a black box. When ICEBs1 integrates into a secondary site, the crossover regions in attICEBs1 and that of the secondary site are not necessarily identical, potentially creating a mismatch. This mismatch, if not repaired, will be resolved by host replication, generating left and right ends with different crossover sequences. Excision would then create a circular ICEBs1 with a heteroduplex in the attachment site on ICEBs1.
