Abstract
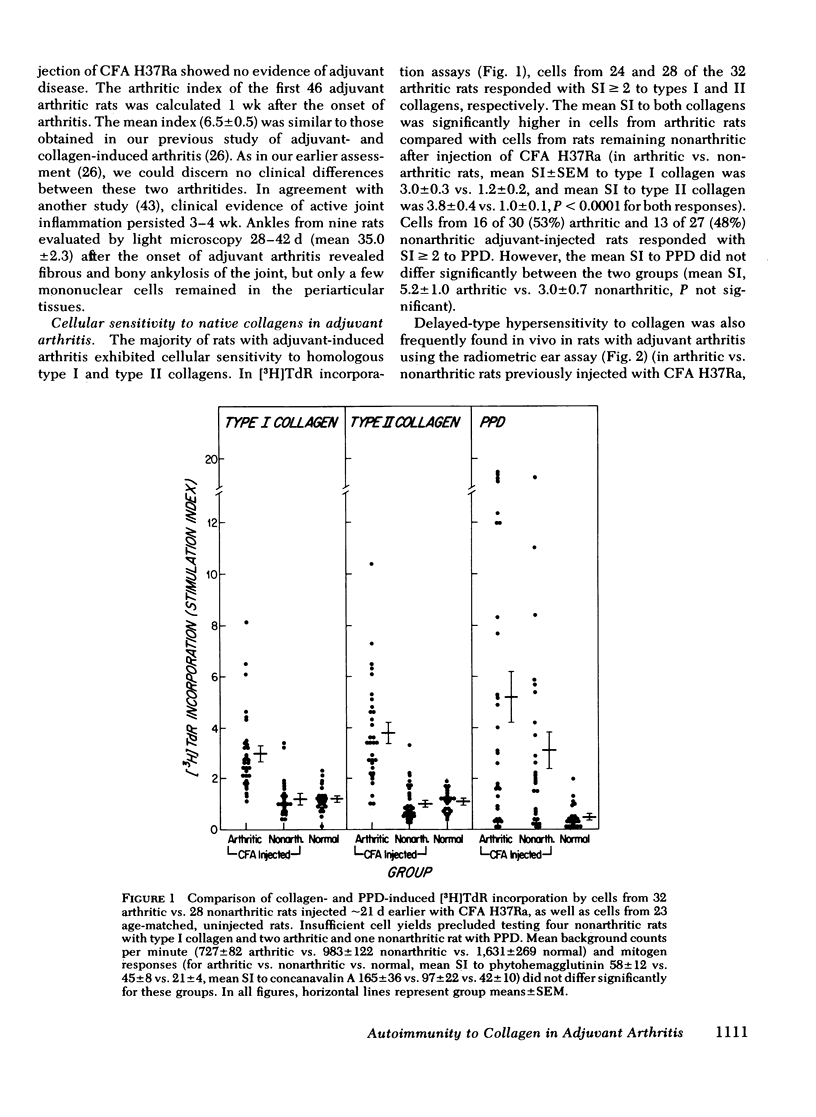
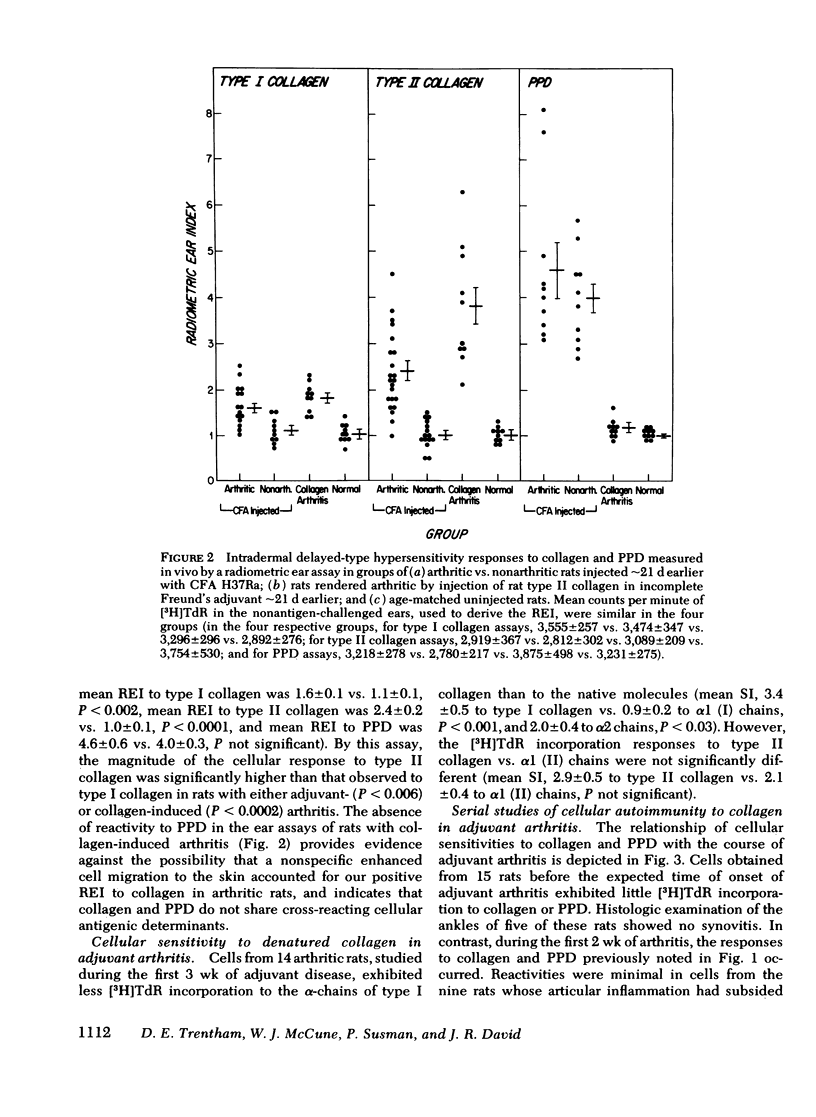
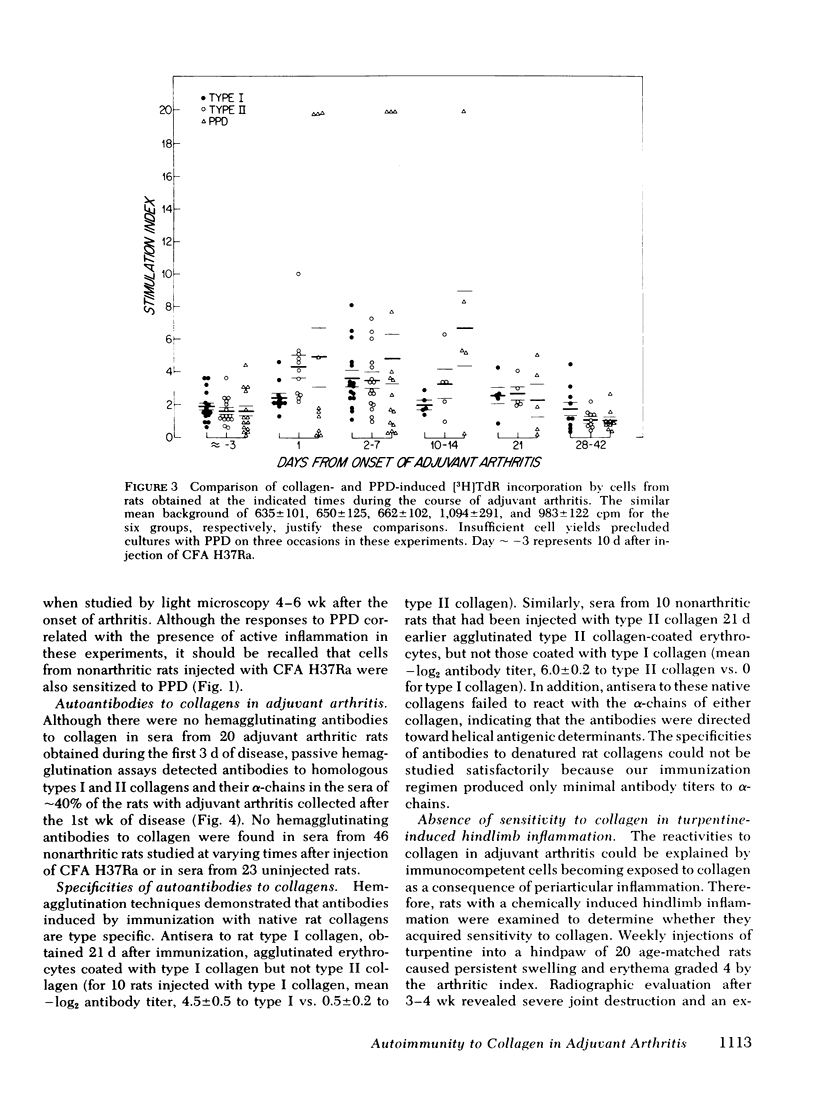
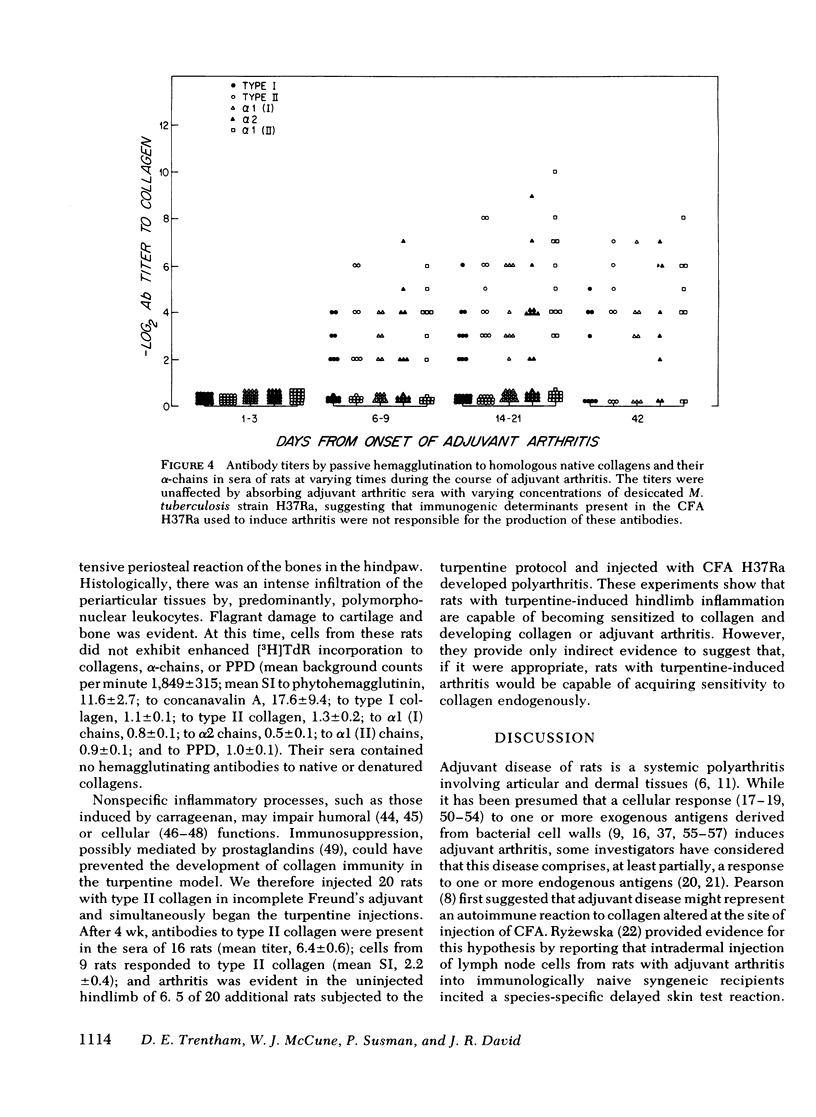
Arthritis can be induced in rats by intradermal injection of oil containing bacterial derivatives (adjuvant-induced arthritis) or cartilage collagen (type II collagen-induced arthritis). It was of interest, therefore, to determine whether collagen functions as an autoantigen in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Blood mononuclear cells from the majority of rats with adjuvant arthritis exhibited enhanced thymidine incorporation to homologous types I and II collagens, as well as to purified protein derivative of tuberculin. In contrast, cells from rats remaining nonarthritic after injection of adjuvant did not respond to collagen, although they did react to tuberculin. Similar results were obtained with a radiometric ear assay used to quantify intradermal delayed-type hypersensitivity in vivo. Using passive hemagglutination, autoantibodies to these collagens and their denatured alpha-chains were frequently detected in the sera of rats late in the course of adjuvant arthritis. Rats with inflammation of a hindlimb induced by turpentine did not acquire sensitivity to collagen. These data indicate that autoimmunity to collagen is a common feature of adjuvant- and collagen-induced arthritis, both of which are considered to be mediated by immunologic mechanisms.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aschheim L., Raffel S. The immunodepressant effect of carrageenin. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Mar;11(3):253–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTEIN N. A., WAKSMAN B. H. THE PATHOGENESIS OF ADJUVANT DISEASE IN THE RAT. I. A HISTOLOGIC STUDY OF EARLY LESIONS IN THE JOINTS AND SKIN. Yale J Biol Med. 1964 Dec;37:177–194. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner W. A., Beck F. W., Lorber A., Pearson C. M., Whitehouse M. W. Adjuvant disease in rats: biochemical criteria for distinguishing several phases of inflammation and arthritis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Feb;145(2):625–630. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry H., Willoughby D. A., Giroud J. P. Evidence for an endogenous antigen in the adjuvant arthritic rat. J Pathol. 1973 Dec;111(4):229–238. doi: 10.1002/path.1711110403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bice D., Schwartz H. J., Lake W. W., Salvaggio J. The effect of carrageenan on the establishment of delayed hypersensitivity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(4):628–636. doi: 10.1159/000230555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. H., Pearson C. M., Abe C. Adjuvant polyarthritis. IV. Induction by a synthetic adjuvant: immunologic, histopathologic, and other studies. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jan;23(1):62–71. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currey H. L., Ziff M. Suppression of adjuvant disease in the rat by heterologous antilymphocyte globulin. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):185–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Giroud J. P., Willoughby D. A. Studies on the mediators of the acute inflammatory response induced in rats in different sites by carrageenan and turpentine. J Pathol. 1971 May;104(1):15–29. doi: 10.1002/path.1711040103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugui E. M., Houssay R. H. Passive transfer of unresponsiveness by lymph node cells. Studies on adjuvant disease. Immunology. 1975 Apr;28(4):703–710. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAX M., WAKSMAN B. H. FURTHER IMMUNOLOGIC STUDIES OF ADJUVANT DISEASE IN THE RAT. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1963;23:331–347. doi: 10.1159/000229438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMANEK K., ROSAK M., STEFFEN C. WEITERE UNTERSUCHUNGEN UEBER DIE EXPERIMENTELLE ADJUVANS-ARTHRITIS DER RATTE. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1964;24:39–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman G. W., Sultzer B. M. Further studies on the activation of lymphocytes by endotoxin protein. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1329–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler N. M. A pathogenetic model for erosive synovitis: lessons from animal arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Mar-Apr;19(2):256–266. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn E., Timpl R., Miller E. J. The production of specific antibodies to native collagens with the chain compositions, (alpha1(I))3, (alpha1(II))3, and (alpha1(I))2alpha 2. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):421–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E., Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Smiley J. D., Ziff M. Immunologic models used for the study of rheumatoid arthritis. Fed Proc. 1973 Feb;32(2):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. I. Evidence for the regulatory function of thymus-derived cells in the induction of the disease. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1878–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. II. Different subpopulations of T lymphocytes functioning in the development of the disease. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostiala A. A. Radiometric ear index test as a measure of delayed-type-hypersensitivity in the rat. Immunology. 1977 Oct;33(4):561–571. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K., Clague R. B., Shaw M. J., Holt P. J. Native type II collagen-induced arthritis in the rat. I. Incidence and humoral response to collagen. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Jun;39(3):285–290. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muirden K. D., Peace G. Light and electron microscope studies in carragheenin, adjuvant, and tuberculin-induced arthris. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Jul;28(4):392–401. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.4.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWBOULD B. B. ROLE OF LYMPH NODES IN ADJUVANT-INDUCED ARTHRITIS IN RATS. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 Sep;23:392–396. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.5.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. Development of arthritis, periarthritis and periostitis in rats given adjuvants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jan;91(1):95–101. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. EXPERIMENTAL JOINT DISEASE OBSERVATIONS ON ADJUVANT-INDUCED ARTHRITIS. J Chronic Dis. 1963 Aug;16:863–874. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(63)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., WAKSMAN B. H., SHARP J. T. Studies of arthritis and other lesions induced in rats by injection of mycobacterial adjuvant. V. Changes affecting the skin and mucous membranes. Comparison of the experimental process with human disease. J Exp Med. 1961 Mar 1;113:485–510. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.3.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., WOOD F. D. PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ADJUVANT ARTHRITIS BY LYMPH NODE OR SPLEEN CELLS. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:547–560. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., WOOD F. D. Studies of arthritis and other lesions induced in rats by the injection of mycobacterial adjuvant. VII. Pathologic details of the arthritis and spondylitis. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jan;42:73–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnham M. J., Schoester G. A., van der Kwast T. H., Benner R. Alterations in granulation tissue growth induced in vivo by lymphocytes from adjuvant-diseased rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;58(2):227–231. doi: 10.1159/000232196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F. Adjuvant arthritis induced by Corynebacterium rubrum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):296–298. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. P., Trentham D. E., McCune W. J., Ginsberg B. I., Reich P., David J. R. Abrogation of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats by psychological stress. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1979;92:218–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumjanek V. M., Watson S. R., Sljivić V. S. A re-evaluation of the role of macrophages in carrageenan-induced immunosuppression. Immunology. 1977 Sep;33(3):423–432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolovic D., Beugnot M. C., Dumont F., Bujadoux M. A new method to measure the specific cellular component of a delayed hypersensitivity response in the ear of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):604–606. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. J., Catanzaro P. J. The differential suppression of antigen, lymphokine and mitogen-induced delayed hypersensitivity-type skin reactions by carrageenan. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(3):409–421. doi: 10.1159/000230948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. J., Leskowitz S. The effect of carrageenan on delayed hypersensitivity reactions. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen C., Formanek K., Timpl R. Hemmung der Adjuvans-Arthritis durch Lathyrismus. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1965 Jun;128(5):451–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen C., Wick G. Delayed hypersensitivity reactions to collagen in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1971;141(2):169–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart-Tull D. E., Shimono T., Kotani S., Kato M., Ogawa Y., Yamamura Y., Koga T., Pearson C. M. The adjuvant activity of a non-toxic, water-soluble glycopeptide present in large quantities in the culture filtrate of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain DT. Immunology. 1975 Jul;29(1):1–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Cremer M. A., Dixit S. N., Kang A. H., Townes A. S. Collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Comparison of vitreous and cartilage-derived collagens. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Apr;22(4):347–352. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Cremer M. A., Kang A. H., Townes A. S. Collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Evaluation of early immunologic events. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Dec;22(12):1344–1351. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. W., Wilson A. R., Cruickshank W. J., Horne C. H. Evaluation of carrageenan as an immunosuppressive agent and mediator of intravascular coagulation. Biomedicine. 1976 May;24(2):102–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Catanese V. M., Rubin D. F. Collagen fractionation: separation of native types I, II and III by differential precipitation. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):114–118. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius R. A., David J. R. Passive transfer by cells of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):359–366. doi: 10.1172/JCI109136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius R. A., Rocklin R. E., David J. R. Cellular sensitivity to collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 17;299(7):327–332. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808172990703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):857–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H., David J. R. Humoral and cellular sensitivity to collagen in type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):89–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Miller J. F., Gamble J., Whitelaw A. A radioisotopic method to measure delayed type hypersensitivity in the mouse. I. Studies in sensitized and normal mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(5):670–692. doi: 10.1159/000231449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., PEARSON C. M., SHARP J. T. Studies of arthritis and other lesions induced in rats by injection of mycobacterial adjuvant. II. Evidence that the disease is a disseminated immunologic response to exogenous antigen. J Immunol. 1960 Oct;85:403–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., WENNERSTEN C. PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ADJUVANT ARTHRITIS IN RATS WITH LIVING LYMPHOID CELLS OF SENSITIZED DONORS. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1963;23:129–139. doi: 10.1159/000229412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD J. R., JONES R. S. Studies on adjuvant-induced polyarthritis in rats. I. Adjuvant composition, route of injection, and removal of depot site. Arthritis Rheum. 1962 Dec;5:557–564. doi: 10.1002/art.1780050604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse D. J., Whitehouse M. W., Pearson C. M. Passive transfer of adjuvant-induced arthritis and allergic encephalomyelitis in rats using thoracic duct lymphocytes. Nature. 1969 Dec 27;224(5226):1322–1322. doi: 10.1038/2241322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood F. D., Pearson C. M., Tanaka A. Capacity of mycobacterial wax D and its subfractions to induce adjuvant arthritis in rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;35(5):456–467. doi: 10.1159/000230198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahiri H., Gagnon J., Ayotte R., Laurin C. A. Adjuvant experimental polyarthritis. Can Med Assoc J. 1969 Sep 6;101(5):269–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


