Figure 4. 3D CLSM images were captured from the gfp-labeled S. maltophilia wild-type (left), rpfF mutant strain (middle) and the rpfF mutant strain supplemented with 100 µM DSF (right).
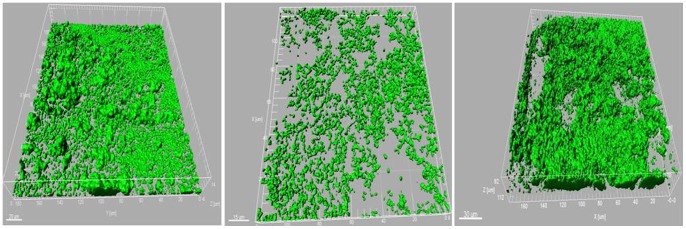
While the wild-type strain formed structured, surface-covering cell architecture with a particular texture consisting of several cell layers, the rpfF mutant strain constructed an unstructured and unconnected monolayer film of cells. The rpfF mutant strain supplemented with 100 µM DSF (cis-Δ2-11-methyl-Dodecenoic Acid), however, formed the same structure observed for the wild-type. gfp-labeled wild-type and rpfF mutant strain cultures as well as the rpfF mutant strain culture supplemented with 100 µM synthetic DSF molecule were grown in LB medium up to OD600 of 1. The cultures were then filled into the chambers of the Lab-Tek® II CC2™ Chamber Slide™ System and incubated at 37°C for three days. To capture the microscopic images a Leica TCS SPE confocal laser scanning microscope was used. The confocal stacks were acquired with the Leica ACS APO 63X OIL CS objective (NA: 1.30) by applying a z-step of 0.4–0.9 µm. The 3D analysis of the CLSM stacks was performed using the software Imaris 7.0. The assay was performed at least four times.
