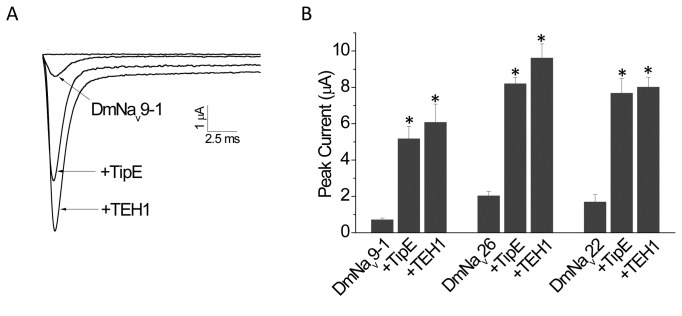
Figure 1. Modulatory effects of TipE and TEH1 on peak sodium currents of DmNav9-1, DmNav22, or DmNav26 channels.
(A) Representative traces of peak sodium currents from oocytes expressing DmNav9-1, DmNav9-1+TipE, and DmNav9-1+TEH1 sodium channels. Note that the sodium current of the DmNav9-1 channel possesses a non-inactivating component, known as persistent current (10% of the maximal transient peak current). Both TipE and TEH1 enhanced the persistent current. However, the persistent current remained to be about 10% of the maximal transient peak current. (B) Both TipE and TEH1 significantly increased peak sodium currents of all three Para sodium variants tested: DmNav9-1, DmNav26, and DmNav22, but there was no significant difference between the effects of TipE and TEH1. Sodium currents were recorded 48 hours after cRNA injection. Sodium currents were recorded by a step depolarization to from -80 to 65 mV in 5mV increments with a holding potential of -120 mV. Data are presented as means ± SEM for 12-15 oocytes. * indicates a significant difference compared to peak of DmNav channel only using one-way ANOVA with Scheffe’s post hoc analysis (p<0.05).