Figure 7. Example decoded hallucinations.
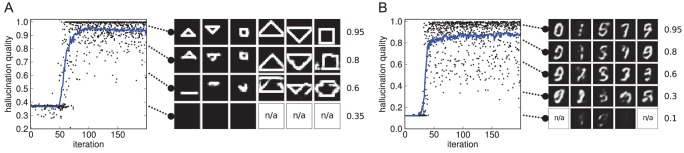
Examples (right-hand side) are shown with corresponding scatter plots for reference (left-hand side; from Figures S1D and 6D). (A) for the model trained on shapes, displayed are examples from the six shape categories (columns, as categorised by matching to the shape templates), for four different qualities (rows, with quality values listed on the right-hand side; images were of that quality or within +0.05 thereof). For entries marked ‘n/a’ there was no hallucination of that type and quality (note that the categories are not really meaningful for lowest quality images anyway). (B) Similar to A, but for the model trained on MNIST. Examples shown were classified as belonging to digit categories 0, 1, 5, 7, and 9 (columns), for five different qualities (rows, annotation as in A). MNIST hallucinations of lower quality often looked like less well-defined digits or mixtures of different digit classes, or they would deviate from the categories in the training set in more subtle ways. Human judgement of quality and class could deviate from the classifier's results in such cases.
