Figure 6.
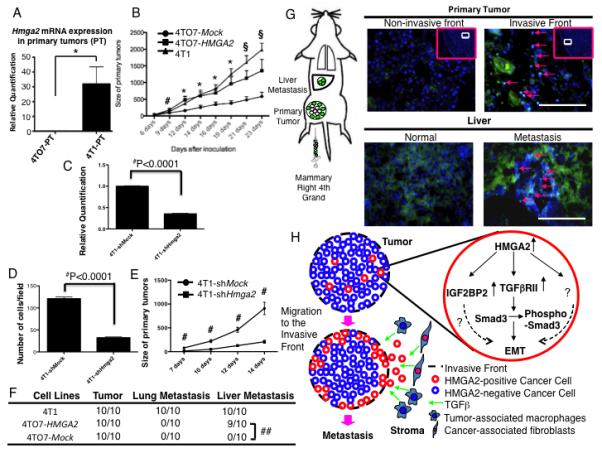
4TO7 cells stably over-expressing HMGA2 form primary tumors more rapidly and can metastasize to the liver. (A) Hmga2 mRNA expression in the primary tumor of 4T1 and 4TO7 derived cells. (B) Primary tumors derived from 4TO7-HMGA2 cells rapidly developed similar to 4T1 cells until 16 days after implantation when compared to 4TO7-Mock cells. #=P<0.05 (4TO7-Mock vs. 4TO7-HMGA2 cells). *=P<0.05 (4TO7-Mock vs. 4TO7-HMGA2 cells and 4TO7-Mock vs. 4T1 cells). §=P<0.05 (4TO7-Mock vs. 4TO7-HMGA2 cells) and P<0.001 (4TO7-Mock vs. 4T1 cells). (C) Hmga2 mRNA expression in 4T1-NTC-shRNA and 4T1-Hmga2-shRNA cells. ##=P<0.0001 (D) A matrigel invasion assay (4T1-NTC-shRNA and 4T1-Hmga2-shRNA cells). The number of “invaded” cells was counted per field (at 100× magnification) in at least 10 different fields per filter. The numbers are shown as mean±SD from two experiments performed in triplicate. ##=P<0.0001. (E) Primary tumors derived from 4T1-Hmga2-shRNA cells slowly developed 7 days after implantation when compared to 4T1-NTC-shRNA cells. #=P<0.001. (F) Liver metastases (arrows) were induced in 4TO7 cells stably over-expressing HMGA2 (4TO7-HMGA2), but not in 4TO7 Mock-transfected (4TO7-Mock) cells (##=P<0.0001). (G) 4TO7-HMGA2 cells were localized to the invasive front (arrows), but not at the non-invasive front of the primary tumor developed from the mixture between 4TO7-Mock and 4TO7-HMGA2 cells. 4TO7-HMGA2 cells were detected in the metastatic liver lesion (liver parenchyma, arrows). Scale bars represent 100 μm. (H) Schematic of HMGA2-induced metastasis. HMGA2 induces expression of the TGFβRII. These cells then undergo EMT, migrate and localize to the invasive front of the tumor where they interact with TGFβ from the stroma facilitating invasion and metastasis.
