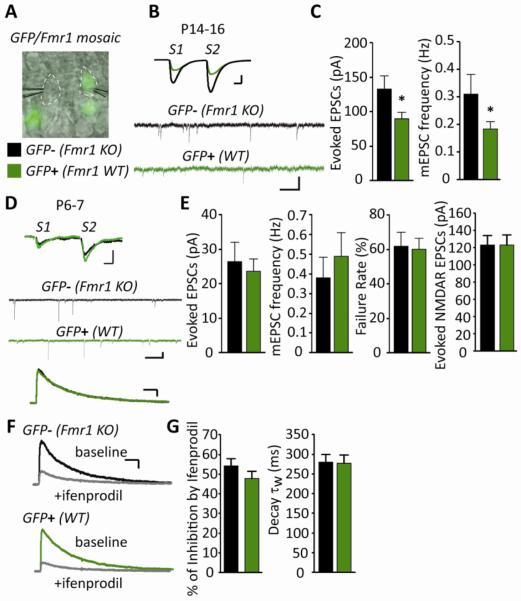
Figure 2. The effects of endogenous postsynaptic FMRP on excitatory synaptic function are developmentally regulated.
(A) Representative DIC and epifluorescence image during simultaneous whole cell recordings from GFP− (Fmr1 KO) and GFP+ (WT) CA1 neurons in acute hippocampal slices from a GFP/Fmr1 mosaic mouse. White dotted lines outline recorded neurons (B) Representative evoked EPSCs and mEPSCs from simultaneous recordings of GFP− (Fmr1 KO) and GFP+ (WT) neurons in acute slices from a P14–16 GFP/Fmr1 mosaic mouse. Scale bars: evoked EPSCs=50pA/10ms; mEPSCs=10pA/500ms. (C) Average EPSC amplitude (n=16 cell pairs) and mEPSC frequency (n=31) are reduced in GFP+ (WT) neurons in comparison to neighboring GFP− (Fmr1 KO) neurons. (D) Representative evoked EPSCs, mEPSCs and evoked, pharmacologically isolated NMDAR-EPSCs from GFP− (Fmr1 KO) and GFP+ (WT) neurons in acute slices from a P6–7 GFP/Fmr1 mosaic mouse. Scale bars: evoked EPSCs=10pA/10ms; mEPSCs=10pA/500ms; NMDAR EPSCs=50pA/100ms. (E) Average evoked EPSC amplitude (p > 0.1), failure rate (n=17; p > 0.1)), mEPSC frequency (n=20; p > 0.1) and evoked NMDAR-mediated EPSC amplitude (n=58; p > 0.1) are not different between GFP− (Fmr1 KO) and GFP+ (WT) neurons at P6–7. (F) Representative evoked NMDAR-mediated EPSCs before and after 3μM ifenprodil (scale bar = 50pA/100ms). (G) Average % inhibition by ifenprodil (n=44; p > 0.1) and weighted time constant (τw) of the decay of NMDAR-EPSCs (n=49; p > 0.1) from GFP− (Fmr1 KO) and GFP+ (WT) neurons at P6–8 are not different. * p< 0.05.