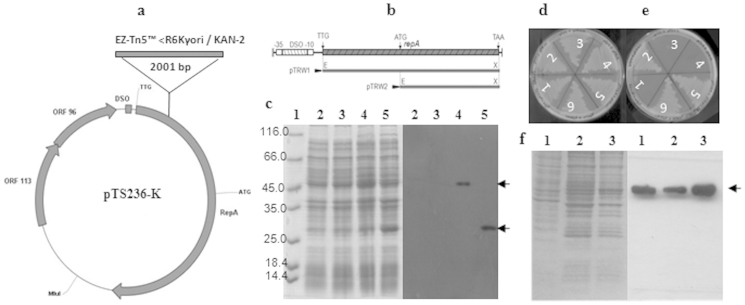
Figure 2.
Panel (a) shows the pTS236-K map with a minitransposon insertion between the predicted start codon UUG and a single AUG codon of repA specifying 165-methionine residue. Arrows indicate the transcriptional orientation of repA, orf106 and orf96. The DSO found upstream of repA start codon UUG is shown as a filled square. Panel (b) shows the physical map of the DSO and repA region of pTS236. DSO is shown as a hatched box. The extent of repA cloned to generate expression plasmids coding RepA (pTRW1) from predicted start codon UUG and from the AUG specifying 165-methionine (pTRW2) are indicated with solid lines. Panel (c) shows an SDS-PAGE and the corresponding western blot probed using anti-His antibody. Lane 1 represents the protein molecular mass marker. Lanes 2 and 3 show protein extracts prepared from uninduced E. coli BL21(DE3) cells having either pTRW1(lane 2) or pTRW2 (lane 3). Lanes 4 and 5 represent similar extracts prepared from induced cultures. RepA-specific signals seen in induced cultures are shown with arrows. Panel (d) and (e) represent replication of pTS236-K in permissive (E. coli pir116) and non-permissive (E. coli BL21) hosts. Panel (d) shows growth on LB with ampicillin and kanamycin plates of E. coli pir116 (pTS236-K) containing expression vector pET23b (sector 1), pTRW1 (sector 2), pTRW2 (sector 3), pTRM (sector 4). Sectors 5 and 6 represent growth of E. coli pir116 (pTRW1) having plasmids pT106M and pT96M, respectively. Growth of E. coli BL21 carrying the same plasmids is shown in panel (e). Panel (f) shows an SDS-PAGE and the corresponding western blots generated using RepA specific antibodies. Lane 1 represents total proteins of Acinetobacter sp. DS002. Lanes 2 and 3 are protein extracts prepared from E. coli BL21 cells expressing RepA from predicted start codon with or without C-terminal histidine tag, respectively.