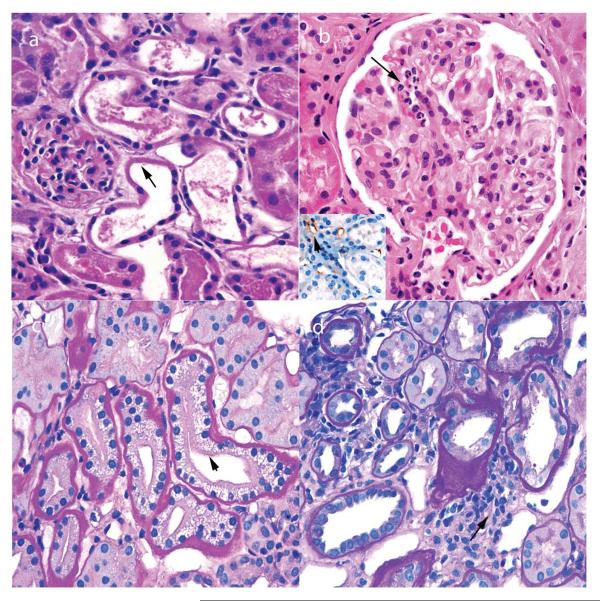
Figure 2.
Pathological findings in renal biopsy samples taken 0–3 days after transplantation. a | Acute tubular injury, with loss of brush borders and nuclei in proximal tubules (arrow) and little infiltrate. These findings also persist beyond 3 days after transplantation in patients with delayed graft function. b | Hyperacute rejection, with neutrophils in glomerular capillaries (arrow). The inset image shows foci of C4d deposition (red staining) in some peritubular capillaries (arrow), but not others (asterisk). c | Acute tubulopathy resulting from the toxic effects of calcineurin inhibitors, with characteristic isometric vacuolization (arrow). This complication can occur at any time after transplantation. d | Urine leaks that cause obstruction typically demonstrate only a focal infiltrate (arrow), but can mimic acute cellular rejection. Permission obtained from Amirsys © Colvin, R. B. et al. Diagnostic Pathology: Kidney Diseases (Salt Lake City, 2011).