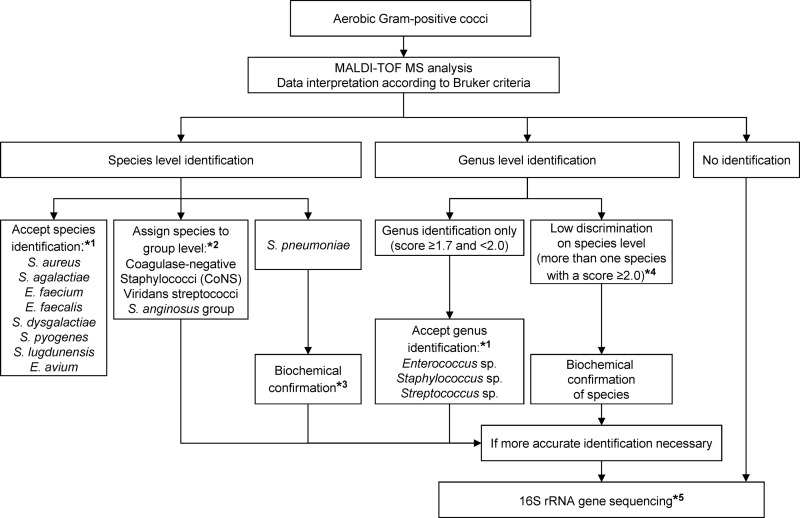
Fig 1.
Algorithm for the identification of Gram-positive cocci in routine diagnostics using MALDI-TOF MS. Recommendations are based on the results of the prospective study, including 1,619 clinical isolates. *1, species and genera with less than five isolates were not integrated in this algorithm, as the numbers are too low to give a proper recommendation. However, all rare isolates were correctly identified by MALDI-TOF MS. It is suggested that these isolates are identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing until sufficient data are available to update the approved lists. *2, group assignment as follows: CoNS, all staphylococcal species except S. aureus and S. lugdunensis; viridans streptococci, alpha-hemolytic streptococcal species except S. pneumoniae; S. anginosus group, S. anginosus/constellatus/intermedius. *3, biochemical confirmation of S. pneumoniae by, e.g., testing of bile solubility and optochin susceptibility. *4, observed for the following streptococci: S. anginosus/constellatus, S. dysgalactiae/pyogenes, S. dysgalactiae/canis, S. equinus/lutetiensis, S. pneumoniae/oralis, and S. vestibularis/salivarius. *5, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and analysis as outlined by Bosshard et al. (1).