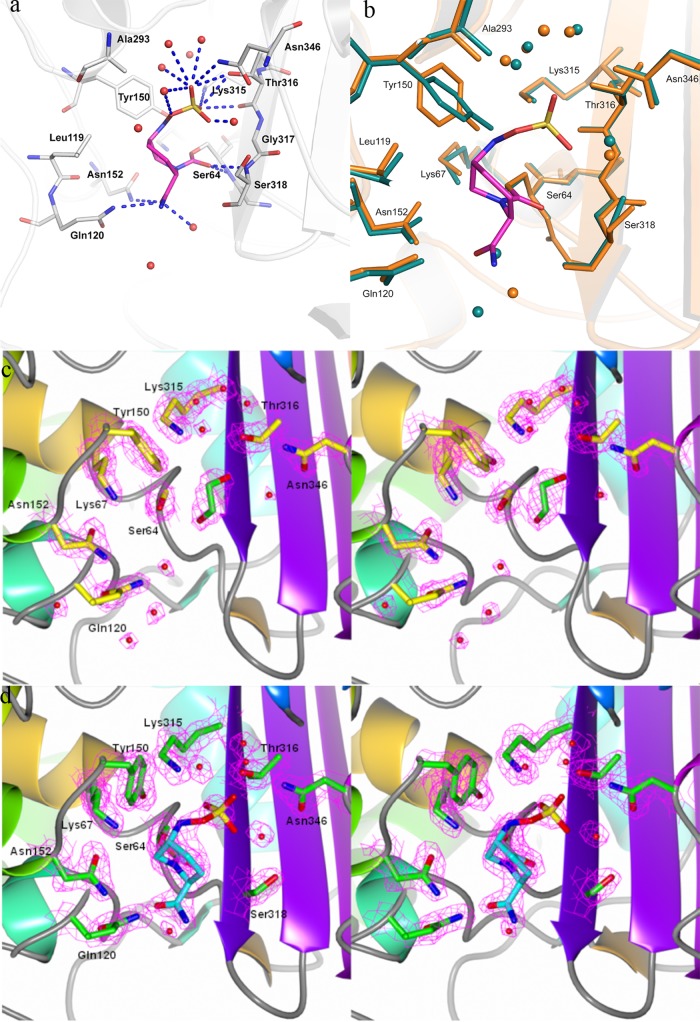
Fig 3.
Avibactam binding pocket on AmpC. (a) Interactions of avibactam in the pocket. Residues within 4 Å are shown as sticks, avibactam is colored magenta, polar interactions are shown as blue dashed lines, and water molecules are depicted as red spheres. (b) Overlay of AmpC bound to avibactam (orange) on the native AmpC structure (green). Avibactam is depicted in magenta sticks, while the water molecules observed close to the pocket are shown as spheres of respective colors. (c) Electron density map of the active site of the P. aeruginosa AmpC native structure. The 2Fo-Fc electron density map of the active-site residues contoured at 1.5 σ level is shown in pink mesh; the residues in the pocket are depicted as yellow sticks, while a cryoprotectant ethylene glycol molecule observed in the pocket has been colored green. (d) Electron density map of the active site of the P. aeruginosa AmpC structure bound to avibactam. The 2Fo-Fc electron density map of the active-site residues contoured at the 1.5 σ level is shown in pink mesh; the residues in the pocket are depicted as green sticks, while avibactam is shown as a cyan stick. Water molecules a, c, and d are depicted as red spheres.