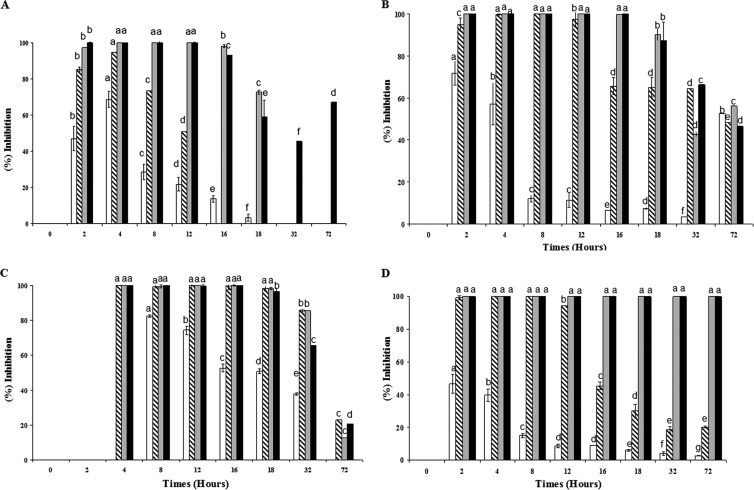
Fig 1.
Inhibition of S. choleraesuis ATCC 14028 (A), P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 (B), Y. enterocolitica ATCC 9610 (C), and E. coli ATCC 35150 (D) growth by colistin at the respective MICs (white, 1× MIC; gray, 2× MIC; diagonal stripes, 3× MIC; black, 4× MIC) in tryptic soy broth as measured by turbidity (OD630). The MICs of colistin for S. choleraesuis ATCC 14028, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, Y. enterocolitica ATCC 9610, and E. coli ATCC 35150 were, respectively, about 1.21, 0.52, 0.4, and 0.12 μg/ml. The IA of colistin was calculated as a percentage as follows: IA = 100 − 100[OD630(x)/OD630(i)], where x is the culture containing colistin and i is the control culture. Means with the same letters are not significantly different (P < 0.05).