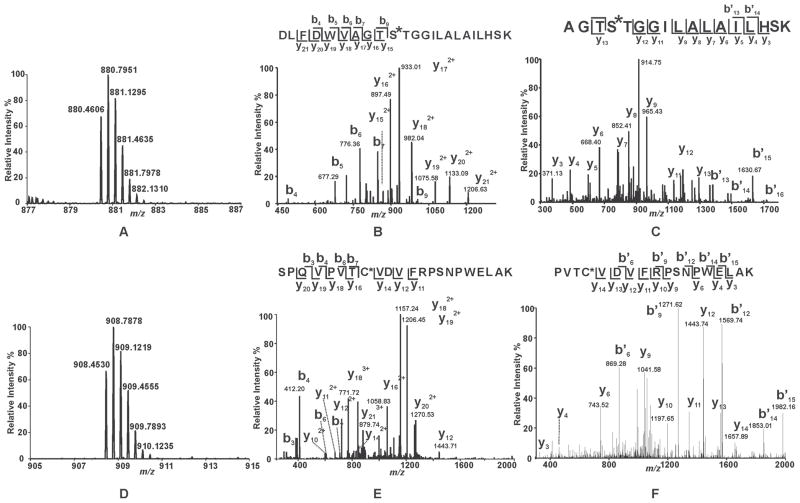
Figure 4. Mass spectral analysis of the tryptic peptides of BEL-modified iPLA2β identifying S465 and C651 as sites of modification.
Purified recombinant iPLA2β was incubated with racemic BEL at a molar ratio of 1:1 at 22°C for 3 min. The reaction was terminated by addition of CHCl3/CH3OH, vortexing, and centrifugation to pellet the precipitated protein. The protein pellet was solubilized in buffer containing RapiGest™, digested with trypsin, and analyzed by LC/MS/MS as described in “Experimental Procedures”. A and D, Full mass spectra showing the presence of unique peaks in the BEL-treated sample in the mass range of m/z 878–887 and 905–915, respectively. B, CID mass spectrum (MS2) of the ion at m/z 880.36 (3+) which corresponds to the BEL-modified tryptic peptide, 456DLFDWVAGTSTGGILALAILHSK478. C, CID mass spectrum (MS3) of the ion at m/z 913. E, CID mass spectrum (MS2) of the ion at m/z 908.36 (3+) which corresponds to the BEL-modified tryptic peptide, 644SPQVPVTCVDVFRPSNPWELAK665. F, CID mass spectrum (MS3) of the ion at m/z 1156. MS2 and MS3 mass spectra in combination with high mass accuracy (< 5 ppm) identify that S465 and C651 are modified by an α-keto-substituted carboxylic acid leading to a mass increase of 254 kDa.