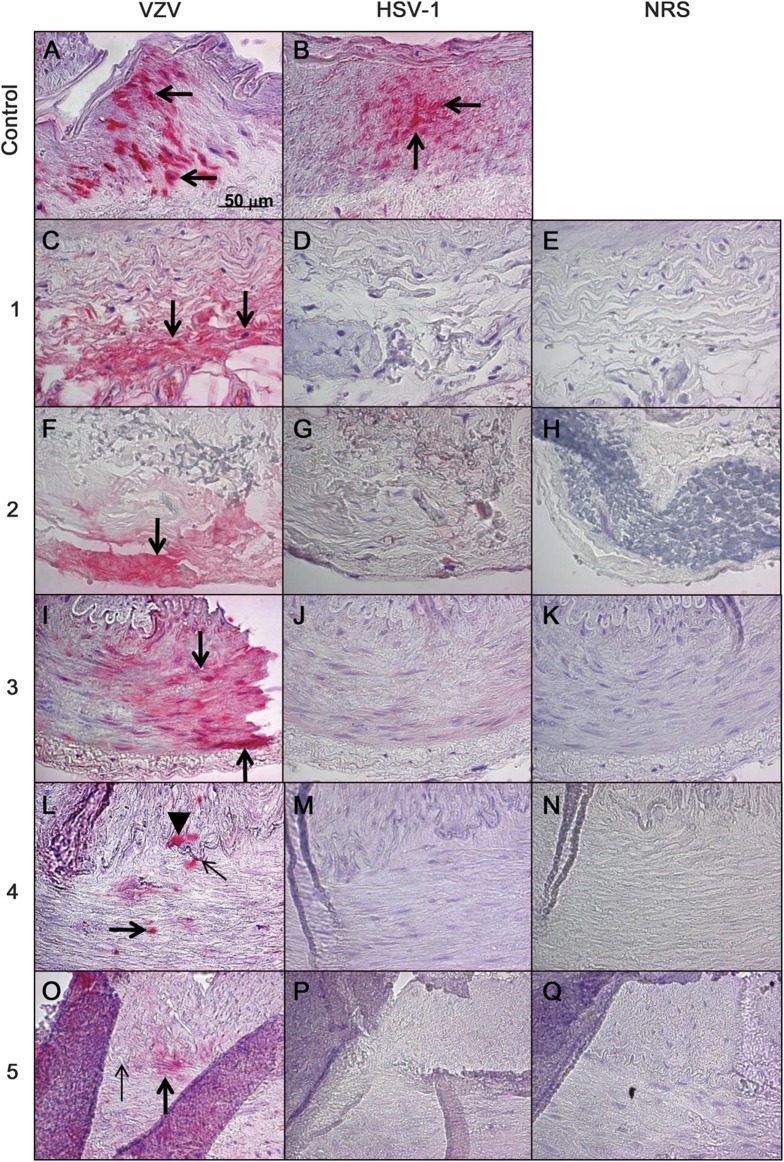
Figure 1. VZV antigen in biopsy-negative temporal arteries from subjects with clinically suspected GCA.
Positive control VZV-infected cadaveric human cerebral artery (A, arrows) shows VZV antigen (pink color). Five (21%) of 24 subjects with suspected GCA, but whose temporal arteries were pathologically GCA negative, contained VZV antigen. Subjects 1 and 2 had VZV antigen exclusively in the adventitia (C and F, respectively, arrows). Subject 3 had VZV antigen exclusively in the media (I, arrows). Subject 4 had VZV antigen in the media (L, thick arrow) and in the intima (L, arrowhead) adjacent to the internal elastic lamina (L, thin arrow). Subject 5 had VZV antigen exclusively in the media (O, thick arrow) adjacent to the internal elastic lamina (O, thin arrow). HSV-1 antigen was present in the positive control HSV-1–infected cadaveric cerebral artery (B, arrows), but not in any human temporal arteries, including those that contained VZV antigen (D, G, J, M, and P). No staining was seen when NRS was used as primary antibody on temporal arteries (E, H, K, N, and Q). None of 13 temporal arteries from 7 normal subjects contained VZV antigen (data not shown). Original magnification ×600. GCA = giant cell arteritis; HSV-1 = herpes simplex virus-1; NRS = normal rabbit serum; VZV = varicella-zoster virus.