Figure 5. RasGEF1B is an interaction partner of Ccdc124.
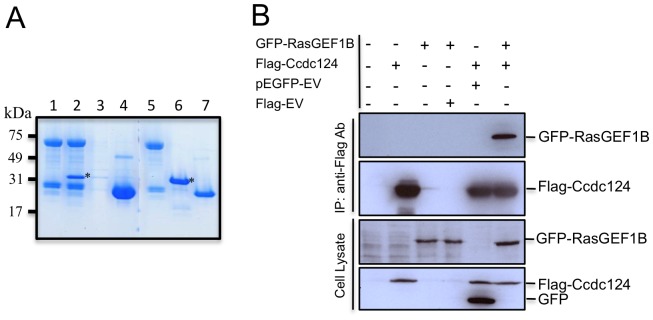
(A) In vitro GST pull-down assay indicating a possible interaction between RasGEF1B and Ccdc124. GST-RasGEF1B protein were immobilized on GSH-beads, followed by incubation with empty PBS buffer control (lane 1), or with bacteria purified His-tagged Ccdc124 (lane 2). As controls, GSH-beads w/o RasGEF1B protein incubated with His-Ccdc124 to monitor the amount of His-Ccdc124 proteins binding to GSH-beads in the absence of a putative interaction partner (lane 3), or GSH-beads immobilized with GST protein and incubated with His-Ccdc124 to monitor interaction capacity of Ccdc124 with GST (lane 4). Lanes 5, 6, 7 are stainings of 100 ng bacteria purified GST-RasGEF1B, His-Ccdc124, and GST proteins, respectively, run in the same gel to monitor their corresponding sizes. Bands corresponding to His-Ccdc124 were marked with asterisks (*). (B) HEK-293 cells were either transfected with Flag-Ccdc124 or GFP-RasGEF1B expression vectors alone or with indicated control plasmids, or alternatively they were co-transfected with Flag-Ccdc124 and GFP-RasGEF1B together, followed by immunoprecipitations (IP) on cell lysates using protein-G beads with anti-Flag antibodies. Subsequently, immunoblots were done on IP or cell lysate samples using anti-GFP (monitoring GFP-RasGEF1B) or anti-Flag-HRP (to assess Flag-Ccdc124) antibodies.
