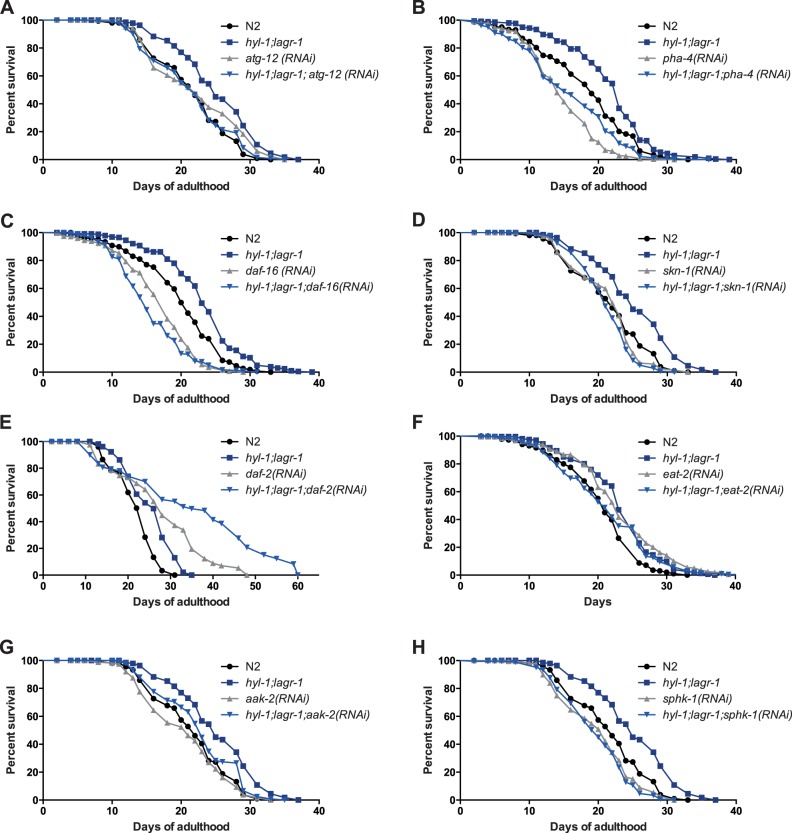
Figure 1. Knock-down of PHA-4, DAF-16, SKN-1, ATG-12, or SPHK-1 affect the extended longevity of hyl-1;lagr-1.
Cumulative survival curves of N2 and hyl-1;lagr-1 worms grown at 20°C subjected to either empty vector control bacteria (L4440) or the indicated RNAi from the early adult stage. (A) When subjected to atg-12 RNAi, the extended lifespan of hyl-1;lagr-1 is normalized to the extent of atg-12(RNAi) control animals, P = 0.3053. (B) When subjected to pha-4 RNAi, the extended lifespan of hyl-1;lagr-1 is normalized to the extent of pha-4(RNAi) control animals, P = 0.2369. (C) When subjected to daf-16 RNAi, the extended lifespan of hyl-1;lagr-1 is decreased beyond the extent of daf-16(RNAi) control animals, P = 0.0002. (D) When subjected to skn-1 RNAi, the extended lifespan of hyl-1;lagr-1 is normalized to the extent of skn-1(RNAi) control animals, P = 0.5476. (E) When subjected to daf-2 RNAi, hyl-1;lagr-1 lifespan is further extended compared to both hyl-1;lagr-1 control animals, P<0.0001, and daf-2(RNAi) control animals, P<0.0001. (F) When subjected to eat-2 RNAi, hyl-1;lagr-1 lifespan is decreased compared to hyl-1;lagr-1 control animals, P = 0.0002, while the lifespan of eat-2(RNAi) animals is extended compared to wild-type control animals, P<0.0001. (G) When subjected to aak-2 RNAi, hyl-1;lagr-1 lifespan is decreased compared to hyl-1;lagr-1 animals, P = 0.0009, while no lifespan effect is seen when comparing aak-2(RNAi) animals to wild-type control animals, P = 0.0975. (H) When subjected to sphk-1 RNAi, the extended lifespan of hyl-1;lagr-1 is normalized to the extent of sphk-1(RNAi) control animals, P = 0.8002. For additional details about these experiments, see Table 1.