Table 1.
I–V parameters for ICa and IBa in control and dfcr IHCs
| IBa (whole-cell) | Control (n= 43) | dfcr (n= 41) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| G (nS) | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 7.0 ± 0.5 | 0.49 |
| V1/2 (mV) | −18.2 ± 0.6 | −19.1 ± 0.7 | 0.30 |
| E (mV) | 48.9 ± 1.0 | 49.1 ± 1.0 | 0.91 |
| k | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 0.57 |
| ICa (whole-cell) | Control (n= 11) | dfcr (n= 13) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| G (nS) | 5.41 ± 0.19 | 5.86 ± 0.37 | 0.30 |
| V1/2 (mV) | −21.4 ± 0.8 | −26.1± 1.0 | 0.002 |
| E (mV) | 43.4 ± 0.8 | 43.3 ± 0.6 | 0.94 |
| k | 6.7 ± 0.3 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 0.26 |
| ICa (perforated- patch) | Control (n= 22) | dfcr (n= 40) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| G (nS) | 5.91 ± 0.25 | 5.98 ± 0.28 | 0.87 |
| V1/2 (mV) | −24.3 ± 0.7 | −27.9 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| E (mV) | 49.6 ± 1.12 | 47.8 ± 0.8 | 0.20 |
| k | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 0.71 |
IBa and ICa were recorded in whole-cell (ruptured patch) or perforated-patch configuration and analysed as described in Methods. I-V relationships were fit with the following equation: 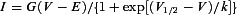 where G is conductance, V is test potential, E is apparent reversal potential, V1/2 is potential of half activation, k is the slope factor. Values represent mean ± SEM. n represents number of IHCs analysed. P values were obtained from unpaired t tests or Wilcoxon rank test.
where G is conductance, V is test potential, E is apparent reversal potential, V1/2 is potential of half activation, k is the slope factor. Values represent mean ± SEM. n represents number of IHCs analysed. P values were obtained from unpaired t tests or Wilcoxon rank test.
