Figure 3.
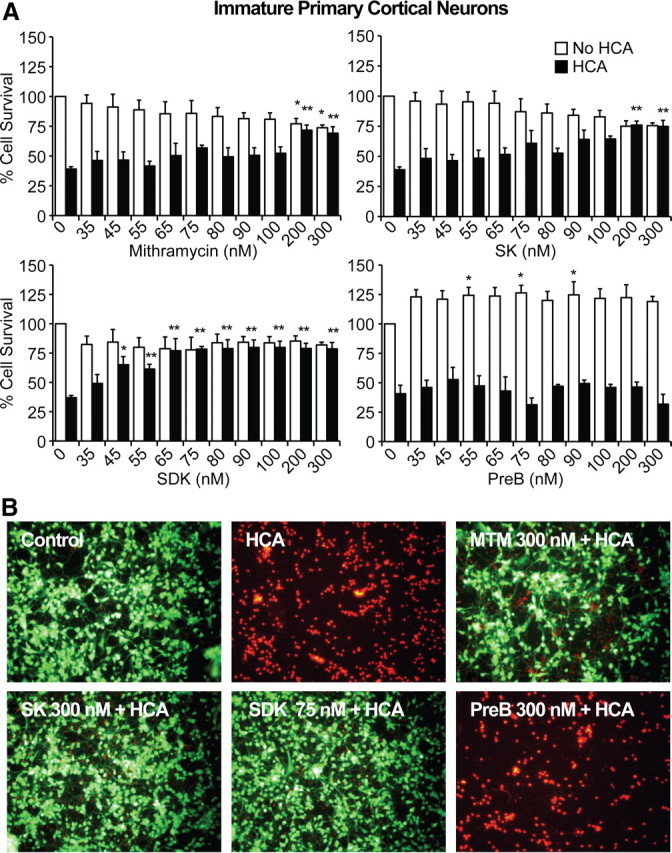
MTM, SK, and SDK protect immature primary cortical neurons (E17) from oxidative stress in a DNA binding-dependent manner. A, MTM, SK, and SDK abrogate neuronal cell death induced by HCA (5 mm) in a dose-dependent manner. SDK was protective at lower doses compared with MTM and SK. In addition, SK and SDK treatment induced no significant toxicity compared with non-HCA control, whereas MTM treatment did. *, Significant death compared with non-HCA control; **, significant protection compared with HCA treatment alone. PreB did not protect primary neurons from HCA-induced cell death. B, Live/Dead staining of treated neuron cultures. Live cells are identified by green, whereas dead cells are identified by red fluorescence.
