Fig. 1.
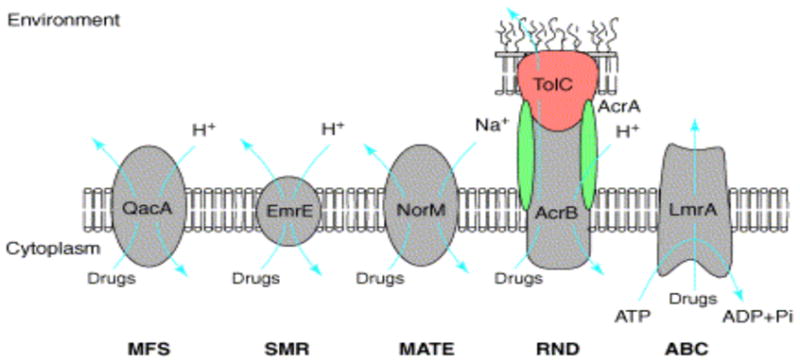
Representative members of the five characterized families of MES [3]. The ABC family including ATP-driven multidrug pumps such as P-glycoprotein and LmrA from Lactococcus lactis. The MFS consists of secondary transporters driven by chemiosmotic energy and includes proton/drug antiporters such as QacA from S. aureus. Both the resistance/nodulation/cell division (RND) and the small multidrug resistance (SMR) families include proton-driven drug efflux pumps such as E. coli AcrB and EmrE, respectively. AcrB functions as a multisubunit complex in association with the outer membrane channel TolC and the membrane fusion protein AcrA. The multidrug and toxic compounds efflux (MATE) family consists of sodium ion-driven drug efflux pumps such as NorM from Vibrio parahaemolyticus.
