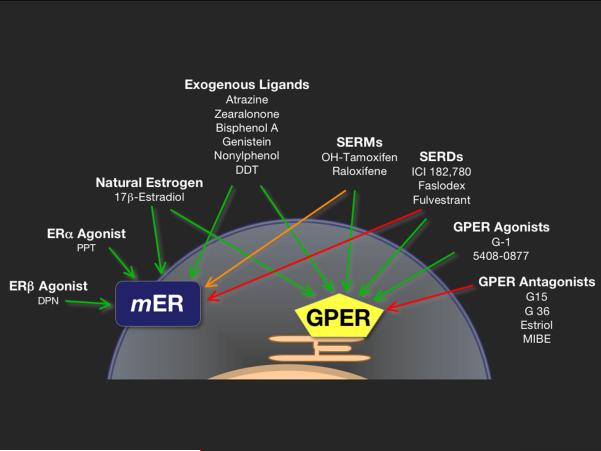
Figure 1.
Agonists and antagonists of membrane-associated subpopulations (mER) of ERα and ERβ, as opposed to GPER with intrinsic activity mediating or inhibiting rapid estrogen signaling. Green arrows: activation, red arrows: inhibition, and the orange arrow: tissue-dependent activation or inhibition. Effects can be achieved by natural (endogenous estrogen such as 17β-estradiol) as well as by synthetic drugs (selective agonists for ERα, ERβ, or GPER), SERMS, SERDs, plant-derived substances (genistein), or highly stable environmental pollutants and xenoestrogens (atrazine, zearalonone, bisphenol A, nonylphenol, or DDT). SERM, selective estrogen receptor modulator; SERD, selective estrogen receptor downregulator. Figure modified from Steroids 2012; 77:935-942. M. Barton: Position paper: The membrane estrogen receptor GPER--Clues and questions, with permission of Elsevier Publishers.