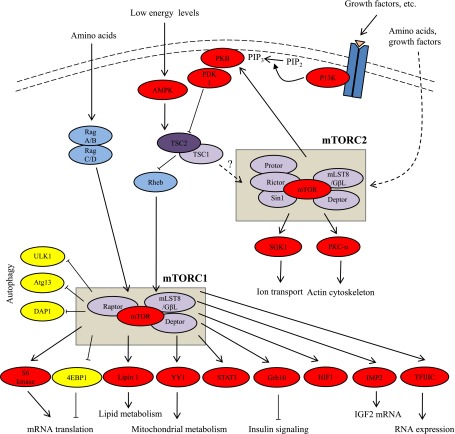
FIG. 1.
mTOR signaling pathways. After stimulation by insulin and other growth factors, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) converts phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3), which localizes PKB to the membrane where it is activated by PDK1 and mTORC2. Activated PKB phosphorylates and inhibits tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC1/2). Rheb, a small GTPase that is inhibited by TSC2, positively modulates mTORC1 activity. mTORC1 phosphorylates S6 kinase 1/2 and 4EBP1, resulting in increased mRNA translation. Amino acid sufficiency activates mTORC1 via Rag A/B and C/D. Under low-energy conditions, the AMP-to-ATP ratio rises and activates AMP kinase (AMPK), which phosphorylates and activates the TSC1/2 complex, resulting in mTORC1 inhibition. mTORC2 activity is mediated via predominantly unknown pathways. mTORC2 phosphorylates and activates PKB, serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 1 (SGK1), and PKC. Arrows, stimulatory effects; block ends, inhibitory effects; solid lines, direct effects, dashed lines, indirect effects. Atg13, autophagy-related protein 13; DAP1, death-associated protein 1; Deptor, DEP domain–containing mTOR-interacting protein; 4EBP, eIF4E-binding protein; GβL- G, protein β-subunit-like protein; HIF1, hypoxia-induced factor 1; IMP2, insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein; mLST8, mammalian lethal with Sec13 protein 8; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; Protor, protein observed with Rictor; Raptor, regulatory associated protein of mTOR; Rictor, rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR; Sin1, stress-activated protein kinase–interacting protein 1; TFIIIC, transcription factor 3C; ULK1, Unc-51–like kinase 1.